Inhibition of RANK signaling in breast cancer induces an anti-tumor immune response orchestrated by CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 33303745
- PMCID: PMC7728758
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20138-8
Inhibition of RANK signaling in breast cancer induces an anti-tumor immune response orchestrated by CD8+ T cells
Abstract
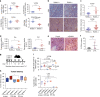
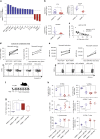
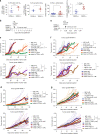
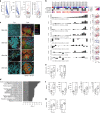
Most breast cancers exhibit low immune infiltration and are unresponsive to immunotherapy. We hypothesized that inhibition of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB (RANK) signaling pathway may enhance immune activation. Here we report that loss of RANK signaling in mouse tumor cells increases leukocytes, lymphocytes, and CD8+ T cells, and reduces macrophage and neutrophil infiltration. CD8+ T cells mediate the attenuated tumor phenotype observed upon RANK loss, whereas neutrophils, supported by RANK-expressing tumor cells, induce immunosuppression. RANKL inhibition increases the anti-tumor effect of immunotherapies in breast cancer through a tumor cell mediated effect. Comparably, pre-operative single-agent denosumab in premenopausal early-stage breast cancer patients from the Phase-II D-BEYOND clinical trial (NCT01864798) is well tolerated, inhibits RANK pathway and increases tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and CD8+ T cells. Higher RANK signaling activation in tumors and serum RANKL levels at baseline predict these immune-modulatory effects. No changes in tumor cell proliferation (primary endpoint) or other secondary endpoints are observed. Overall, our preclinical and clinical findings reveal that tumor cells exploit RANK pathway as a mechanism to evade immune surveillance and support the use of RANK pathway inhibitors to prime luminal breast cancer for immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
R.S. reports non-financial support from Merck and Bristol Myers Squibb; research support from Merck, Puma Biotechnology, and Roche; and personal fees from BMS for an advisory board meeting and from Roche for an advisory board related to a trial-research project. H.A.A. is advisory board at Roche and current employee of Innate Pharma. E.G.S. and G.J.L. have served on advisory boards for Amgen and has received honoraria and research funding from Amgen. S.L. receives research funding from Novartis, Merck, BMS, Roche-Genentech, Puma Biotechnology, Pfizer, and uncompensated advisory board of Novartis, Merck, BMS, Roche-Genentech, Puma Biotechnology, Pfizer, and Seattle Genetics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gonzalez-Suarez E, et al. RANK overexpression in transgenic mice with mouse mammary tumor virus promoter-controlled RANK increases proliferation and impairs alveolar differentiation in the mammary epithelia and disrupts lumen formation in cultured epithelial acini. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007;27:1442–1454. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01298-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

