Kdm6a suppresses the alternative activation of macrophages and impairs energy expenditure in obesity
- PMID: 33303977
- PMCID: PMC8167088
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-020-00694-8
Kdm6a suppresses the alternative activation of macrophages and impairs energy expenditure in obesity
Abstract
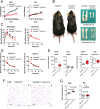
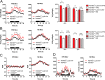
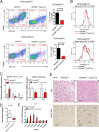
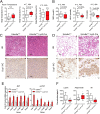
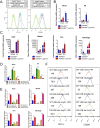
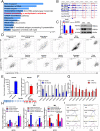
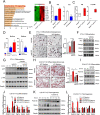
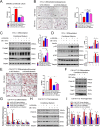
Histone lysine demethylase 6a (Kdm6a) mediates the removal of repressive trimethylation from histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) to activate target gene expression. Obesity is associated with metabolic inflammation, and adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs) are key players orchestrating metabolic inflammation. However, it is still unclear whether the Kdm6a pathway in ATMs regulates energy homeostasis. Here, we identified Kdm6a as a critical epigenetic switch that modulates macrophage polarisation and further disrupts energy balance. Myeloid-specific Kdm6a knockout in Kdm6aF/Y;Lyz2-Cre mice significantly reversed the high-fat diet (HFD)-induced M1-M2 imbalance in white adipose tissue (WAT) and blocked HFD-induced obesity. The brown adipose tissue (BAT) activity, WAT browning and energy expenditure were significantly increased in Kdm6aF/Y;Lyz2-Cre mice. Furthermore, Kdm6a regulated the Ire1α expression in a demethylase activity-dependent manner and augmented the M2 polarisation of macrophages. Macrophage with higher Kdm6a significantly promotes adipogenesis in white adipocyte and inhibits thermogenesis in beige adipocytes. These results suggest that the Kdm6a in macrophages drives obesity and metabolic syndrome by impairing BAT activity and WAT differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

