The Influence of Basic Psychological Needs and Passion in Promoting Elite Young Football Players' Development
- PMID: 33304293
- PMCID: PMC7701099
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.570584
The Influence of Basic Psychological Needs and Passion in Promoting Elite Young Football Players' Development
Abstract
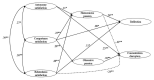
Motivational variables and cognitive skills have been identified as important in an athlete's development. The aim of this study is to explore the influence of each basic psychological needs satisfaction on player's development regarding reflection and concentration disruption with the mediation of types of passion in Spanish young elite football players. A total of 487 elite U18 male football players (Mage = 17.43, SD = 0.71) completed measures of basic psychological needs satisfaction, passion for football, reflective thinking, and concentration disruption. Measurement models were defined using exploratory structural equation models. The results provide support for the model, where each psychological needs satisfaction prompted reflection and had a negative influence on concentration disruption with the mediation of harmonious passion. In addition, obsessive passion mediated the positive relationship between competence satisfaction and concentration disruption. Finally, competence and relatedness satisfaction influenced the development of reflection directly and positively and, exclusively, relatedness satisfaction had a negative influence in a direct way on concentration disruption. In sum, our results highlight that (a) the environment of young footballers through psychological needs satisfaction has a positive (i.e., reflection) or negative (i.e., concentration disruption) influence on the field, but only with the mediation of harmonious passion, (b) in a competitive environment, the perception of competence can have a positive influence on concentration disruption, but only with the development of obsessive passion as a mediator, and (c) relatedness satisfaction plays a key role in distinguishing between reflection and concentration disruption.
Keywords: concentration disruption; dualistic model of passion; motivation; reflective thinking; self-determination theory; self-regulation.
Copyright © 2020 Chamorro, Moreno, García-Calvo and Torregrossa.
Figures
References
-
- Alcaraz-Ibañez M., Sicilia A., Lirola M. J., Burgueño R. (2016). Effects of satisfaction and thwarting of basic psychological needs on the forms of passion for exercise. Psychol. Soc. Educ. 8, 257–272.
-
- Balaguer I., Castillo I., Duda J. L. (2008). Autonomy support, needs satisfaction, motivation and well-being in competitive athletes: a test of the self-determination theory. Rev. de Psicol. del Deporte. 17, 123–139.
-
- Bartels J. M., Magun-Jackson S. (2009). Approach–avoidance motivation and metacognitive self-regulation: the role of need for achievement and fear of failure. Learn. Individ. Differ. 19, 459–463. 10.1016/j.lindif.2009.03.008 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

