Factors Related to Maternal Adverse Outcomes in Pregnant Women with Cardiac Disease in Low-resource Settings
- PMID: 33304394
- PMCID: PMC7709001
- DOI: 10.15420/ecr.2020.04
Factors Related to Maternal Adverse Outcomes in Pregnant Women with Cardiac Disease in Low-resource Settings
Abstract
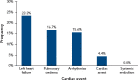
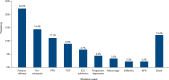
Background: Cardiac disease is an important life-threatening complication during pregnancy. It is frequently seen in pregnant women living in resource-limited areas and often results in premature death. Aim: The aim of this hospital-based longitudinal study was to identify factors related to adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes in pregnant women with cardiac disease in low-resource settings. Methods: The study enrolled 91 pregnant women with congenital or acquired cardiac disease over a period of 2 years in Kenya. Results: Maternal and early neonatal deaths occurred in 12.2% and 12.6% of cases, respectively. The risk of adverse outcomes was significantly increased in those with pulmonary oedema (OR 11, 95% CI [2.3.52]; p=0.002) and arrhythmias (OR 16.9, 95% CI [2.5.113]; p=0.004). Limited access to care was significantly associated with adverse maternal outcomes (p≤0.001). Conclusion: Many factors contribute to adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes in pregnant women with cardiac disease. Access to comprehensive specialised care may help reduce cardiac-related complications during pregnancy.
Keywords: Adverse outcomes; cardiac disease and pregnancy; cardiac events; obstetric events; resource-limited settings; therapeutic abortion.
Copyright © 2020, Radcliffe Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Regitz-Zagrosek V, Roos-Hesselink JW, Bauersachs J et al. 2018 ESC guidelines for the management of cardiovascular diseases during pregnancy: the Task Force for the Management of Cardiovascular Diseases During Pregnancy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3165–241. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy340. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources