Hypoxia and extracellular vesicles: A review on methods, vesicular cargo and functions
- PMID: 33304471
- PMCID: PMC7710128
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12002
Hypoxia and extracellular vesicles: A review on methods, vesicular cargo and functions
Abstract
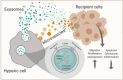
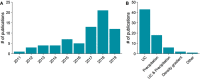
Hypoxia is an essential hallmark of several serious diseases such as cardiovascular and metabolic disorders and cancer. A decline in the tissue oxygen level induces hypoxic responses in cells which strive to adapt to the changed conditions. A failure to adapt to prolonged or severe hypoxia can trigger cell death. While some cell types, such as neurons, are highly vulnerable to hypoxia, cancer cells take advantage of a hypoxic environment to undergo tumour growth, angiogenesis and metastasis. Hypoxia-induced processes trigger complex intercellular communication and there are now indications that extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a fundamental role in these processes. Recent developments in EV isolation and characterization methodology have increased the awareness of the importance of EV purity in functional and cargo studies. Cell death, a hallmark of severe hypoxia, is a known source of intracellular contaminants in isolated EVs. In this review, methodological aspects of studies investigating hypoxia-induced EVs are critically evaluated. Key concerns and gaps in the current knowledge are highlighted and future directions for studies are set. To accelerate and advance research, an in-depth analysis of the functions and cargo of hypoxic EVs, compared to normoxic EVs, is provided with the focus on the altered microRNA contents of the EVs.
Keywords: cancer; exosomes; hypoxia; infarction; intercellular communication; mesenchymal stem cells; microRNA.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
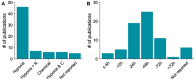
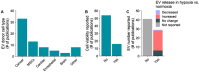
References
-
- Bang, C. , Batkai, S. , Dangwal, S. , Gupta, S. K. , Foinquinos, A. , Holzmann, A. , … Thum, T. (2014). Cardiac fibroblast‐derived microRNA passenger strand‐enriched exosomes mediate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 124(5), 2136–2146. 10.1172/JCI70577 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

