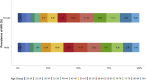
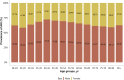
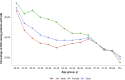
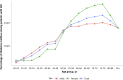
China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2016 Annual Data Report
- PMID: 33304640
- PMCID: PMC7716083
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kisu.2020.09.001
China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2016 Annual Data Report
Figures

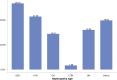
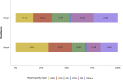
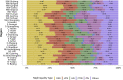
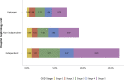


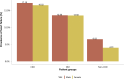

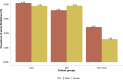

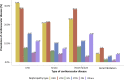
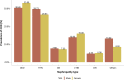

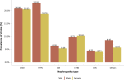
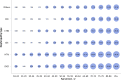
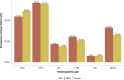

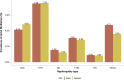




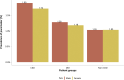

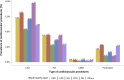
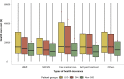
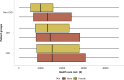

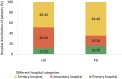
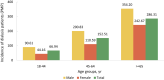
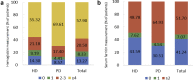

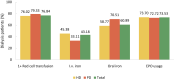
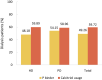
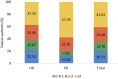
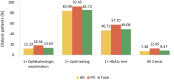
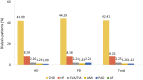
References
-
- Zhang L., Wang F., Wang L. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet (London, England) 2012;379:815–822. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z.H. Nephrology in china. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9:523–528. - PubMed
-
- Yang C., Kong G., Wang L. Big data in nephrology: Are we ready for the change? Nephrology (Carlton) 2019;24:1097–1102. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

