Graded doses of grape seed methanol extract attenuated hepato-toxicity following chronic carbamazepine treatment in male Wistar rats
- PMID: 33304829
- PMCID: PMC7711278
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.11.006
Graded doses of grape seed methanol extract attenuated hepato-toxicity following chronic carbamazepine treatment in male Wistar rats
Abstract
Aim: This study investigated the effects of co-administration of carbamazepine (CBZ) with grape (Vitis vinifera) seed methanolic extract (GSME) on liver toxicity.
Method: Thirty-five male rats (145-155 g) were randomized into 5 groups (n = 7) and administered with propylene glycol (PG 0.1 mL/day), CBZ (25 mg/kg), CBZ (25 mg/kg) + GSME (200 mg/kg), CBZ (25 mg/kg) + GSME (100 mg/kg), or CBZ (25 mg/kg) + GSME (50 mg/kg) orally for 28 days. Twenty-four hours after the last dose, changes in the body weights were determined. The rats were euthanized by cervical dislocation. The liver was weighed and later homogenized; while the supernatant was analyzed biochemically. The liver tissues were preserved in 10 % neutral-buffered formalin for the histomorphological investigation.
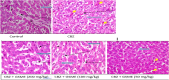
Result: There was significant (p = 0.0001) decrease in the body weight following carbamazepine treatment. The relative liver weight also decreased significantly (p = 0.0004) across the treatment group compared with control. The activities of the liver enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, and glutathione activities), including the concentrations of malondialdehyde, increased significantly (p ≤ 0.0004) following carbamazepine treatment. Various morphological alterations were observed, especially in the photomicrograph of the CBZ treated rats. However, these derangements were attenuated significantly in the CBZ - GSME co-treated group.
Conclusion: This study concludes that GSME treatment may serve as a potential therapeutic agent in carbamazepine-induced hepatotoxicity/ dysfunction.
Keywords: Antiepileptic-drugs; Carbamazepine; Grape seed methanolic extract; Hepatotoxicity.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kaddumukasa M., Mugeny L., Kaddumukasa M.N., Ddumba E., Devereaux M., Furlan A., Sajatovic M., Katabira E. Prevalence and incidence of neurological disorders among adult Ugandans in rural and urban Mukono district; a cross-sectional study. BMC Neurol. 2016;16:227. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0732-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources