Long-term outcomes of abdominal paraganglioma
- PMID: 33304858
- PMCID: PMC7704273
- DOI: 10.4174/astr.2020.99.6.315
Long-term outcomes of abdominal paraganglioma
Abstract
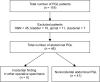
Purpose: Paragangliomas (PGL) are rare neuroendocrine tumors derived from chromaffin cells of the autonomic nervous system. We aim to describe our experience and the long-term outcome of abdominal PGL over the last decade.
Methods: A retrospective review of patients diagnosed with PGL in our hospital between November 2005 and June 2017 was conducted. All nonabdominal PGL were excluded and the clinicopathological features and long-term outcomes of the patients were analyzed.
Results: A total of 46 patients were diagnosed with abdominal PGL. The average age of diagnosis was 55.4 years and there was no sex predilection. The average tumor size was 5.85 cm and they were predominantly located in the infrarenal position (50%). The mean follow-up period was 42 months (range, 1.8-252 months). All patients with metastases had Pheochromocytoma of the Adrenal Gland Scaled Score (PASS) of ≥4. One patient presented with synchronous metastases while 2 developed local recurrence and distant metastases. One presented with only local recurrence. One patient died 5 years after diagnosis.
Conclusion: Abdominal PGL is a rare tumor with excellent long-term prognosis. Recurrence although uncommon, can occur decades after initial diagnosis. Long-term follow-up is therefore recommended for all patients with PGL, especially in patients with PASS of ≥4.
Keywords: Paraganglioma; Recurrence; Surgery; Therapy.
Copyright © 2020, the Korean Surgical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Predictors of Malignancy in Patients with Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2017 Nov;24(12):3624-3630. doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-6074-1. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28884434
-
Predicting Metastatic Potential in Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Comparison of PASS and GAPP Scoring Systems.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Dec 1;105(12):e4661-70. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa608. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32877928 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: a population level analysis of long-term survival over two decades.J Surg Oncol. 2013 May;107(6):659-64. doi: 10.1002/jso.23297. Epub 2012 Dec 11. J Surg Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23233320
-
Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma: Is This a Genetic Disorder?Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019 Jul 31;21(9):104. doi: 10.1007/s11886-019-1184-y. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31367972 Review.
-
A Somatic HIF2α Mutation-Induced Multiple and Recurrent Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma with Polycythemia: Clinical Study with Literature Review.Endocr Pathol. 2017 Mar;28(1):75-82. doi: 10.1007/s12022-017-9469-4. Endocr Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28116635 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas: Review of current diagnosis and treatment options.Cancer Med. 2023 Jul;12(13):13942-13957. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6010. Epub 2023 May 5. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37145019 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pillai S, Gopalan V, Smith RA, Lam AK. Updates on the genetics and the clinical impacts on phaeochromocytoma and paraganglioma in the new era. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;100:190–208. - PubMed
-
- Lenders JW, Duh QY, Eisenhofer G, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Grebe SK, Murad MH, et al. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:1915–1942. - PubMed
-
- Lenders JW, Eisenhofer G, Mannelli M, Pacak K. Phaeochromocytoma. Lancet. 2005;366:665–675. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Sippel RS, O'Dorisio MS, Vinik AI, Lloyd RV, Pacak K, et al. The North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society consensus guideline for the diagnosis and management of neuroendocrine tumors: pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, and medullary thyroid cancer. Pancreas. 2010;39:775–783. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Galan SR, Kann PH. Genet ics and molecular pathogenesis of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2013;78:165–175. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources