Effects of Selenium Nanoparticles Combined With Radiotherapy on Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 33304892
- PMCID: PMC7701302
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.598997
Effects of Selenium Nanoparticles Combined With Radiotherapy on Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of selenium nanoparticles (nano-Se) combined with radiotherapy on the proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) A549 and NCI-H23 cells.
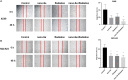
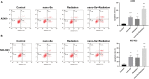
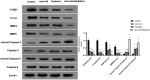
Methods: Nano-Se was synthesized and characterized by transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffractometer, and Ultraviolet-visible (UV)-Vis Spectroscopy, separately. The uptake of nano-Se by lung cancer cells was detected by flow cytometry. Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) method was used to detect the antiproliferative activity of nano-Se combined with radiotherapy. Wound healing tests and transwell assay were used to detect the migration and invasion ability of the cells. Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)/Propidium iodide (PI) staining by flow cytometry was used to detect apoptosis. The expression of Cyclin D1 (CCND1), c-Myc, matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), MMP9, cleaved Caspase-3, and cleaved Caspase-9 were detected by Western blot.
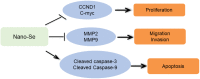
Results: The average diameter of nano-Se was 24.39 nm and the wavelength of nano-Se increased with the increase of radiation dose under UV-Vis Spectroscopy. The uptake of nano-Se in lung cancer cells was increased with the increase of nano-Se concentration. The nano-Se combined with radiotherapy decreased the proliferation activity of NSCLC cell lines A549 and NCI-H23 in a dose-dependent manner (all P < 0.05). Compared with the Control group, nano-Se combined with radiotherapy could significantly inhibit the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells (all P < 0.05), and the effects of the combination of nano-Se and radiotherapy was better than that of a single application (all P < 0.05). Furthermore, nano-Se combined with radiotherapy could induce apoptosis of lung cancer cells (P < 0.05) and nano-Se combined with radiotherapy could significantly inhibit the expression of proliferation-related proteins CCND1, c-Myc, invasion and migration-related proteins MMP2 and MMP9, but conversely promoted the expression of apoptosis-related proteins cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9. Conclusion: This study found that nano-Se combined with radiotherapy plays an anti-cancer role in lung cancer cells by inhibiting cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as inducing apoptosis, suggesting that nano-Se may be used as a radiosensitizer in the clinical treatment of lung cancer, but further research is still needed.
Keywords: combination; lung cancer; radiotherapy; selenium nanoparticle; synergistic therapy.
Copyright © 2020 Tian, Wei, Zhang and Xu.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Honokiol combined with curcumin sensitizes multidrug-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma A549/DDP cells to cisplatin.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Nov;22(5):1301. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10736. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34630656 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA combined with adriamycin inhibited malignant biological behaviors of NSCLC A549 cell line in a synergistic way.BMC Cancer. 2016 Nov 18;16(1):899. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2921-x. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27863471 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of nadroparin with radiotherapy results in powerful synergistic antitumor effects in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells.Oncol Rep. 2016 Oct;36(4):2200-6. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4990. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27498922
-
Lappaconitine sulfate induces apoptosis and G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest by PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells.Acta Histochem. 2020 Jul;122(5):151557. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151557. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Acta Histochem. 2020. PMID: 32622431
-
Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 indicates poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cell proliferation and invasion.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(9):2671-2679. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_14963. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29771418
Cited by
-
Change in the serum selenium level of patients with non-metastatic and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) during radiotherapy as a predictive factor for survival.Strahlenther Onkol. 2025 Jun;201(6):616-626. doi: 10.1007/s00066-024-02276-w. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Strahlenther Onkol. 2025. PMID: 39240366 Free PMC article.
-
Mycosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Penicillium tardochrysogenum as a therapeutic agent and their combination with infrared irradiation against Ehrlich carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 31;14(1):2547. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52982-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38291218 Free PMC article.
-
The landscape of m6A regulators in esophageal cancer: molecular characteristics, immuno-oncology features, and clinical relevance.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(24):1347. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5895. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36660671 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting Metastasis and Improving Chemosensitivity via Chitosan-Coated Selenium Nanoparticles for Brain Cancer Therapy.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 29;12(15):2606. doi: 10.3390/nano12152606. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35957037 Free PMC article.
-
Antifibrotic Effect of Selenium-Containing Nanoparticles on a Model of TAA-Induced Liver Fibrosis.Cells. 2023 Nov 28;12(23):2723. doi: 10.3390/cells12232723. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai W., Mastrandrea N., Tham K., Monks T., Lau S. (2014). Pentoxifylline induces GSK-3β−independent proteasomal degradation of cyclin D1 and arrests renal cancer cells in the G1 phase (616.5). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 54 223–235. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

