Mitochondrial RNA in Alzheimer's Disease Circulating Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 33304899
- PMCID: PMC7701247
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.581882
Mitochondrial RNA in Alzheimer's Disease Circulating Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
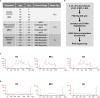
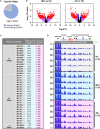
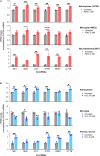
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common type of dementia. Amyloid β (Aβ) plaques, tau-containing neurofibrillary tangles, and neuronal loss leading to brain atrophy are pathologic hallmarks of AD. Given the importance of early diagnosis, extensive efforts have been undertaken to identify diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for AD. Circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs) provide a platform for "liquid biopsy" biomarkers for AD. Here, we characterized the RNA contents of plasma EVs of age-matched individuals who were cognitively normal (healthy controls (HC)) or had mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to AD or had mild AD dementia (AD). Using RNA sequencing analysis, we found that mitochondrial (mt)-RNAs, including MT-ND1-6 mRNAs and other protein-coding and non-coding mt-RNAs, were strikingly elevated in plasma EVs of MCI and AD individuals compared with HC. EVs secreted from cultured astrocytes, microglia, and neurons after exposure to toxic conditions relevant to AD pathogenesis (Aβ aggregates and H2O2), contained mitochondrial structures (detected by electron microscopy) and mitochondrial RNA and protein. We propose that in the AD brain, toxicity-causing mitochondrial damage results in the packaging of mitochondrial components for export in EVs and further propose that mt-RNAs in plasma EVs can be diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for MCI and AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biomarker; extracellular vesicles; mitochondrial RNA; mitochondrial protein.
Copyright © 2020 Kim, Meng, Perez de Acha, Mustapic, Cheng, Eren, Kundu, Piao, Munk, Wood, De, Noh, Delannoy, Cheng, Abdelmohsen, Kapogiannis and Gorospe.
Figures



References
-
- Albert M. S., DeKosky S. T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H. H., Fox N. C., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7 270–279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andaloussi S. E. L., Mäger I., Breakefield X. O., Wood M. J. (2013). Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 12 347–357. - PubMed
-
- Athauda D., Gulyani S., Karnati H. K., Li Y., Tweedie D., Mustapic M., et al. (2019). Utility of neuronal-derived exosomes to examine molecular mechanisms that affect motor function in patients with parkinson disease: a secondary analysis of the Exenatide-PD Trial. JAMA Neurol. 76 420–429. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beal M. F. (1998). Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1366 211–223. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

