Phage Therapy as Adjuvant to Conservative Surgery and Antibiotics to Salvage Patients With Relapsing S. aureus Prosthetic Knee Infection
- PMID: 33304911
- PMCID: PMC7701306
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.570572
Phage Therapy as Adjuvant to Conservative Surgery and Antibiotics to Salvage Patients With Relapsing S. aureus Prosthetic Knee Infection
Abstract
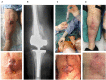
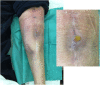
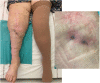
Objectives: To report the management of three consecutive patients with relapsing Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic knee infection (PKI) for whom explantation was not feasible who received a phage therapy during a "Debridement Antibiotics and Implant Retention" (DAIR) procedure followed by suppressive antimicrobial therapy. Methods: Each case was discussed individually in our reference center and with the French National Agency (ANSM). The lytic activity of three phages targeting S. aureus, which was produced with a controlled and reproducible process, was assessed before surgery (phagogram). A hospital pharmacist extemporaneously assembled the phage cocktail (1 ml of 1 × 1010 PFU/ml for each phage) as "magistral" preparation (final dilution 1 × 109 PFU/ml), which was administered by the surgeon directly into the joint, after the DAIR procedure and joint closure (PhagoDAIR procedure). Results: Three elderly patients were treated with the PhagoDAIR procedure. Phagograms revealed a high susceptibility to at least two of the three phages. During surgery, all patients had poor local conditions including pus in contact to the implant. After a prolonged follow-up, mild discharge of synovial fluid persisted in two patients, for whom a subsequent DAIR was performed showing only mild synovial inflammation without bacterial persistence or super-infection. The outcome was finally favorable with a significant and impressive clinical improvement of the function. Conclusions: The PhagoDAIR procedure has the potential to be used as salvage for patients with relapsing S. aureus PKI, in combination with suppressive antibiotics to avoid considerable loss of function. This report provides preliminary data supporting the setup of a prospective multicentric clinical trial.
Keywords: S. aureus; bacteriophages; phage therapy; phagotherapy; prosthetic-joint infection.
Copyright © 2020 Ferry, Kolenda, Batailler, Gustave, Lustig, Malatray, Fevre, Josse, Petitjean, Chidiac, Leboucher and Laurent.
Figures



References
-
- Société de Pathologie Infectieuse de Langue Française (SPILF) Collège des Universitaires de Maladies Infectieuses et Tropicales (CMIT) Groupe de Pathologie Infectieuse Pédiatrique (GPIP) Société Française d'Anesthésie et de Réanimation (SFAR) Société Française de Chirurgie Orthopédique et Traumatologique (SOFCOT) Société Française d'Hygiène Hospitalière (SFHH) Société Française de Médecine Nucléaire (SFMN) et al. Recommendations for bone and joint prosthetic device infections in clinical practice (prosthesis, implants, osteosynthesis). société de pathologie infectieuse de langue française. Med Mal Infect. (2010) 40:185–211. 10.1016/j.medmal.2009.12.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ariza J, Cobo J, Baraia-Etxaburu J, Benito N, Bori G, Cabo J, et al. . Executive summary of management of prosthetic joint infections. clinical practice guidelines by the Spanish society of infectious diseases and clinical microbiology (SEIMC). Enferm Infect Microbiol Clin. (2017) 35:189–95. 10.1016/j.eimce.2017.02.013 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferry T, Boucher F, Fevre C, Perpoint T, Chateau J, Petitjean C, et al. . Innovations for the treatment of a complex bone and joint infection due to XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa including local application of a selected cocktail of bacteriophages. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2018) 73:2901–3. 10.1093/jac/dky263 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

