Prospective Study of Long Noncoding RNA, MGAT3-AS1, and Viremia of BK Polyomavirus and Cytomegalovirus in Living Donor Renal Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 33305115
- PMCID: PMC7710814
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.09.005
Prospective Study of Long Noncoding RNA, MGAT3-AS1, and Viremia of BK Polyomavirus and Cytomegalovirus in Living Donor Renal Transplant Recipients
Abstract
Introduction: Viremia after renal transplantation is a major cause of morbidity and mortality and treatment opportunities are limited. Tests to determine the increased risk for viremia would be preferable.
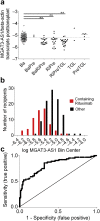
Methods: In a prospective, single-center study, we conducted follow-up of 163 renal transplant recipients after incident living donor renal transplantation. We determined a long noncoding RNA, β-1,4-mannosylglycoprotein 4-β-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-antisense1 (MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratio), in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Viremia of BK polyomavirus and cytomegalovirus was diagnosed with more than 1000 plasma copies/ml within the first 3 postoperative months. The MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratio was assessed before viremia was determined.
Results: Receiver operator characteristics curve analysis showed a median MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratio cutoff value of 4.45 × 10-6 to indicate viremia after transplantation. Samples for 11 of 66 renal transplant recipients (17%) with MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratios below 4.45 × 10-6 showed viremia of BK polyomavirus and cytomegalovirus compared with only 6 of 97 renal transplant recipients (6%) with higher MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratios (odds ratio [OR]: 3.03; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.06-8.67 by Fisher exact test). Furthermore, samples for 6 of 66 renal transplant recipients (9%) with MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratios below 4.45 × 10-6 showed BK polyomavirus viremia compared with none of 97 renal transplant recipients (0%) with higher MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratios (OR: 20.95; 95% CI, 1.16-378.85 by Fisher exact test). Multivariate logistic regression analysis confirmed that MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratios below the cutoff level remained significantly associated with viremia after transplant. Lower MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratios occurred with rituximab-containing induction therapy.
Conclusions: A low MGAT3-AS1/beta-actin ratio indicates an increased risk for viremia of BK polyomavirus and cytomegalovirus in living donor renal transplant recipients.
Keywords: BK polyomavirus; cytomegalovirus; living-donor renal transplant recipients; long noncoding RNA.
© 2020 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Fishman J.A. Infection in solid-organ transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2601–2614. - PubMed
-
- Leeaphorn N., Garg N., Thamcharoen N. Cytomegalovirus mismatch still negatively affects patient and graft survival in the era of routine prophylactic and preemptive therapy: a paired kidney analysis. Am J Transplant. 2019;19:573–584. - PubMed
-
- Karuthu S., Blumberg E.A. Common infections in kidney transplant recipients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7:2058–2070. - PubMed
-
- Brennan D.C. Cytomegalovirus in renal transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:848–855. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

