Cytosolic calcium regulates cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 through Calpain-A and Importin α3
- PMID: 33305734
- PMCID: PMC7748415
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60132
Cytosolic calcium regulates cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 through Calpain-A and Importin α3
Abstract
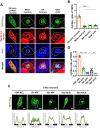
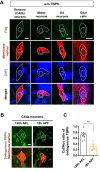
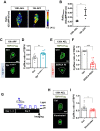
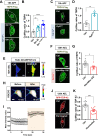
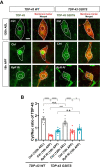
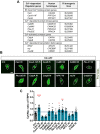
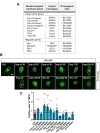
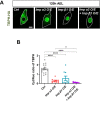
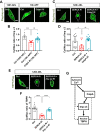
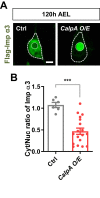
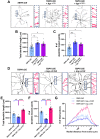
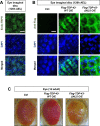
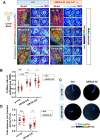
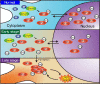
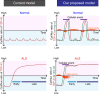
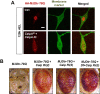
Cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 in motor neurons is the most prominent pathological feature in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). A feedback cycle between nucleocytoplasmic transport (NCT) defect and TDP-43 aggregation was shown to contribute to accumulation of TDP-43 in the cytoplasm. However, little is known about cellular factors that can control the activity of NCT, thereby affecting TDP-43 accumulation in the cytoplasm. Here, we identified via FRAP and optogenetics cytosolic calcium as a key cellular factor controlling NCT of TDP-43. Dynamic and reversible changes in TDP-43 localization were observed in Drosophila sensory neurons during development. Genetic and immunohistochemical analyses identified the cytosolic calcium-Calpain-A-Importin α3 pathway as a regulatory mechanism underlying NCT of TDP-43. In C9orf72 ALS fly models, upregulation of the pathway activity by increasing cytosolic calcium reduced cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 and mitigated behavioral defects. Together, these results suggest the calcium-Calpain-A-Importin α3 pathway as a potential therapeutic target of ALS.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Drosophila; TDP-43; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; calcium; calpain; neuroscience; nucleocytoplasmic transport.
© 2020, Park et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JP, CC, SP, DL, KK, YJ, EK, JC, YJ, CS, HK, DH, SL No competing interests declared
Figures




References
-
- Allemand E, Dokudovskaya S, Bordonné R, Tazi J. A conserved Drosophila transportin-serine/arginine-rich (SR) protein permits nuclear import of Drosophila SR protein splicing factors and their antagonist repressor splicing factor 1. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2002;13:2436–2447. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-02-0102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amlie-Wolf A, Ryvkin P, Tong R, Dragomir I, Suh E, Xu Y, Van Deerlin VM, Gregory BD, Kwong LK, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Wang LS, Lee EB. Transcriptomic changes due to cytoplasmic TDP-43 expression reveal dysregulation of histone transcripts and nuclear chromatin. PLOS ONE. 2015;10:e0141836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141836. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2018R1A2B6001607/Ministry of Science and ICT, South Korea/International
- 2019R1A4A1024278/Ministry of Science and ICT, South Korea/International
- KRISS-2019-GP2019-0018/Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science/International
- 20-BR-04-02/Ministry of Science and ICT, South Korea/International
- IBS-R013-A1/Ministry of Science and ICT, South Korea/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

