Distinct effects of complement and of NLRP3- and non-NLRP3 inflammasomes for choroidal neovascularization
- PMID: 33305736
- PMCID: PMC7732340
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60194
Distinct effects of complement and of NLRP3- and non-NLRP3 inflammasomes for choroidal neovascularization
Abstract
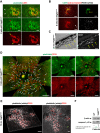
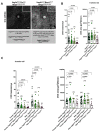
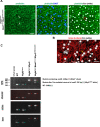
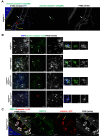
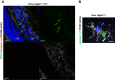
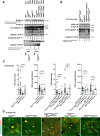
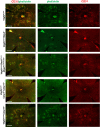
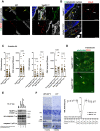
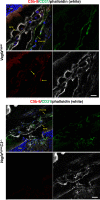
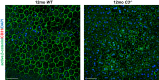
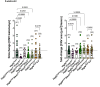
NLRP3 inflammasome activation and complement-mediated inflammation have been implicated in promoting choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), but central questions regarding their contributions to AMD pathogenesis remain unanswered. Key open questions are (1) whether NLRP3 inflammasome activation mainly in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) or rather in non-RPE cells promotes CNV, (2) whether inflammasome activation in CNV occurs via NLRP3 or also through NLRP3-independent mechanisms, and (3) whether complement activation induces inflammasome activation in CNV. Here we show in a neovascular AMD mouse model that NLRP3 inflammasome activation in non-RPE cells but not in RPE cells promotes CNV. We demonstrate that both NLRP3-dependent and NLRP3-independent inflammasome activation mechanisms induce CNV. Finally, we find that complement and inflammasomes promote CNV through independent mechanisms. Our findings uncover an unexpected role of non-NLRP3 inflammasomes for CNV and suggest that combination therapies targeting inflammasomes and complement may offer synergistic benefits to inhibit CNV.
Keywords: NLRP3; VEGF-A; caspase-1; choroidal neovascularization; complement; immunology; inflammasome; inflammation; mouse; neovascular age-related macular degeneration.
© 2020, Malsy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JM, AA, JL, KS, AM No competing interests declared
Figures
References
-
- Brydges SD, Mueller JL, McGeough MD, Pena CA, Misaghi A, Gandhi C, Putnam CD, Boyle DL, Firestein GS, Horner AA, Soroosh P, Watford WT, O'Shea JJ, Kastner DL, Hoffman HM. Inflammasome-mediated disease animal models reveal roles for innate but not adaptive immunity. Immunity. 2009;30:875–887. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calippe B, Augustin S, Beguier F, Charles-Messance H, Poupel L, Conart JB, Hu SJ, Lavalette S, Fauvet A, Rayes J, Levy O, Raoul W, Fitting C, Denèfle T, Pickering MC, Harris C, Jorieux S, Sullivan PM, Sahel JA, Karoyan P, Sapieha P, Guillonneau X, Gautier EL, Sennlaub F. Complement factor H inhibits CD47-Mediated resolution of inflammation. Immunity. 2017;46:261–272. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.01.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

