Behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal products among the public in response to Covid-19 in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 33306725
- PMCID: PMC7732085
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243706
Behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal products among the public in response to Covid-19 in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
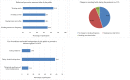
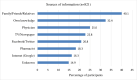
The present study was conducted to assess the behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal foods/products among the public in response to Covid-19. A cross-sectional survey comprised of 1222 participants was conducted from 27 June to 20 July 2020. Kruskal-Wallis test was used to identify the differences in behavioral preventive practices across different demographic categories. To identify the factors associated with the use of preventive medicines and herbal foods/products, multivariable logistic regression was performed. Most participants adopted the recommended preventive practices such as washing hands more frequently (87.5%), staying home more often (85.5%), avoiding crowds (86%), and wearing masks (91.6%). About half of the smokers reported a decreased rate of smoking during the pandemic. Also, 14.8% took medicines, 57.6% took herbal foods/products, and 11.2% took both medicines and herbal foods/products as preventive measure against Covid-19. Arsenicum album, vitamin supplements, and zinc supplements were the most commonly used preventive medicines. Gender, age, and fear of Covid-19 were significantly associated with the use of both preventive medicines and herbal foods/products. For the management of Covid-19 related symptoms, paracetamol, antihistamines, antibiotics, and mineral (zinc and calcium) supplements were used most often. Most participants sought information from non-medical sources while using medicines and herbal products. Moreover, potentially inappropriate and unnecessary use of certain drugs was identified.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Timeline: WHO's COVID-19 response 2020 [cited 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/interact....
-
- Worldometer. Worldometer; [cited 2020 30 July]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/.
-
- Bangladesh Should Listen to its Health Workers. Human Rights Watch. June 21, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

