Evidence of subclinical quantitative retinal layer abnormalities in AQP4-IgG seropositive NMOSD
- PMID: 33307967
- PMCID: PMC8200372
- DOI: 10.1177/1352458520977771
Evidence of subclinical quantitative retinal layer abnormalities in AQP4-IgG seropositive NMOSD
Abstract
Background: Prior studies have suggested that subclinical retinal abnormalities may be present in aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G (AQP4-IgG) seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), in the absence of a clinical history of optic neuritis (ON).
Objective: Our aim was to compare retinal layer thicknesses at the fovea and surrounding macula between AQP4-IgG+ NMOSD eyes without a history of ON (AQP4-nonON) and healthy controls (HC).
Methods: In this single-center cross-sectional study, 83 AQP4-nonON and 154 HC eyes were studied with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT).
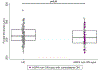
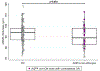
Results: Total foveal thickness did not differ between AQP4-nonON and HC eyes. AQP4-nonON eyes exhibited lower outer nuclear layer (ONL) and inner photoreceptor segment (IS) thickness at the fovea (ONL: -4.01 ± 2.03 μm, p = 0.049; IS: -0.32 ± 0.14 μm, p = 0.029) and surrounding macula (ONL: -1.98 ± 0.95 μm, p = 0.037; IS: -0.16 ± 0.07 μm, p = 0.023), compared to HC. Macular retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL: -1.34 ± 0.51 μm, p = 0.009) and ganglion cell + inner plexiform layer (GCIPL: -2.44 ± 0.93 μm, p = 0.009) thicknesses were also lower in AQP4-nonON compared to HC eyes. Results were similar in sensitivity analyses restricted to AQP4-IgG+ patients who had never experienced ON in either eye.
Conclusions: AQP4-nonON eyes exhibit evidence of subclinical retinal ganglion cell neuronal and axonal loss, as well as structural evidence of photoreceptor layer involvement. These findings support that subclinical anterior visual pathway involvement may occur in AQP4-IgG+ NMOSD.
Keywords: Neuromyelitis optica; aquaporin-4; fovea; optical coherence tomography; retina.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures

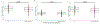
References
-
- You Y, Zhu L, Zhang T, et al. Evidence of Müller Glial Dysfunction in Patients with Aquaporin-4 Immunoglobulin G-Positive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. Ophthalmology 2019; 126: 801–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

