Potential predictors of type-2 diabetes risk: machine learning, synthetic data and wearable health devices
- PMID: 33308172
- PMCID: PMC7733701
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-020-03763-4
Potential predictors of type-2 diabetes risk: machine learning, synthetic data and wearable health devices
Abstract
Background: The aim of a recent research project was the investigation of the mechanisms involved in the onset of type 2 diabetes in the absence of familiarity. This has led to the development of a computational model that recapitulates the aetiology of the disease and simulates the immunological and metabolic alterations linked to type-2 diabetes subjected to clinical, physiological, and behavioural features of prototypical human individuals.
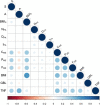
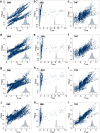
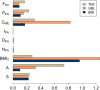
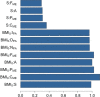
Results: We analysed the time course of 46,170 virtual subjects, experiencing different lifestyle conditions. We then set up a statistical model able to recapitulate the simulated outcomes.
Conclusions: The resulting machine learning model adequately predicts the synthetic dataset and can, therefore, be used as a computationally-cheaper version of the detailed mathematical model, ready to be implemented on mobile devices to allow self-assessment by informed and aware individuals. The computational model used to generate the dataset of this work is available as a web-service at the following address: http://kraken.iac.rm.cnr.it/T2DM .
Keywords: Computational modeling; Emulator; Machine learning; Random forest; Synthetic data; T2D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Organization, W.H. Media Centre. http://who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/. Accessed 27 Sept 2016
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

