Hormographiella aspergillata: an emerging basidiomycete in the clinical setting? A case report and literature review
- PMID: 33308180
- PMCID: PMC7731474
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05679-z
Hormographiella aspergillata: an emerging basidiomycete in the clinical setting? A case report and literature review
Abstract
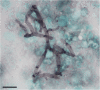
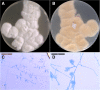
Background: Filamentous basidiomycetes are mainly considered to be respiratory tract colonizers but the clinical significance of their isolation in a specimen is debatable. Hormographiella aspergillata was first reported as a human pathogen in 1971. We discuss the role of this mold as a pathogen or colonizer and give an update on diagnostic tools and in vitro antifungal susceptibility.
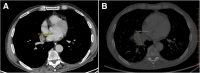
Case presentation: We identified three cases of H. aspergillata with respiratory symptoms in a short period of time. One invasive infection and two colonizations were diagnosed. Culture supernatants showed that H. aspergillata can produce galactomannan and β-D-glucan but not glucuronoxylomannan. For the first time, isavuconazole susceptibility was determined and high minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were found. Liposomal amphotericin B and voriconazole have the lowest MICs.
Conclusion: To date, 22 invasive infections involving H. aspergillata have been reported. On isolation of H. aspergillata, its pathogenic potential in clinical settings can be tricky. Molecular identification and antifungal susceptibility testing are essential considering high resistance against several antifungal therapies.
Keywords: Antifungal susceptibility; Basidiomycete; Coprinus cinereus; Fungal colonization; Hormographiella aspergillata; Mould.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Gené J, Guillamon JM, Guarro J, Pujol I, Ulfig K. Molecular characterization, relatedness and antifungal susceptibility of the basidiomycetous Hormographiella species and Coprinus cinereus from clinical and environmental sources. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1996;70(1):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00393569. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nenoff P, Friedrich T, Schwenke H, Mierzwa M, Horn LC, Haustein UF. Rare fatal simultaneous mould infection of the lung caused by Aspergillus flavus and the basidiomycete Coprinus sp. in a leukemic patient. J Med Vet Mycol Bi-Mon Publ Int Soc Hum Anim Mycol. 1997;35(1):65–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

