Survival rate of patients with bladder cancer and its related factors in Kurdistan Province (2013-2018): a population-based study
- PMID: 33308221
- PMCID: PMC7733243
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-020-00769-1
Survival rate of patients with bladder cancer and its related factors in Kurdistan Province (2013-2018): a population-based study
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer is one of the most common urinary tract cancers. This study aims to estimate the survival rate of patients with bladder cancer according to the Cox proportional hazards model based on some key relevant variables.
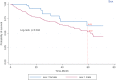
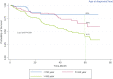
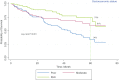
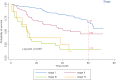
Methods: In this retrospective population-based cohort study that explores the survival of patients with bladder cancer and its related factors, we first collected demographic information and medical records of 321 patients with bladder cancer through in-person and telephone interviews. Then, in the analysis phase, Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test were used to draw the survival curve, compare the groups, and explore the effect of risk factors on the patient survival rate using Cox proportional hazards model.
Results: The median survival rate of patients was 63.2 (54.7-72) months and one, three and five-year survival rates were 87%, 68% and 54%, respectively. The results of multiple analyses using Cox's proportional hazards model revealed that variables of sex (male gender) (HR = 11.8, 95% CI: 0.4-100.7), more than 65 year of age (HR = 4.1, 95% CI: 0.4-11), occupation, income level, (HR = 0.4, 95% CI: 0.2-0.8), well differentiated tumor grade (HR = 3.2, 95% CI: 1.7-6) and disease stage influenced the survival rate of patients (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The survival rate of patients with bladder cancer in Kurdistan province is relatively low. Given the impact of the disease stage on the survival rate, adequate access to appropriate diagnostic and treatment services as well as planning for screening and early diagnosis, especially in men, can increase the survival rate of patients.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Cox proportional hazards model; Population based; Survival rate.
Conflict of interest statement
No direct or indirect commercial, personal, academic, political, religious or ethical incentive is associated with publishing this article.
Figures

References
-
- Koosha A, Farahbakhsh M, Hakimi S, Abdolahi L, Golzari M, Farshad MS. Epidemiologic assessment of cancer disease in East Azerbaijan 2007. Med J Tabriz Univ Med Sci Health Serv. 2010;32(4):74–9.
-
- Salehi A, Khezri AA, Malekmakan L, Aminsharifi A. Epidemiologic status of bladder cancer in Shiraz, southern Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12(5):1323–7. - PubMed
-
- Mahdavi S, Amoori N, Salehiniya H, Almasi Z, Enayatrad M. Trend of bladder cancer mortality in Iran (2006 to 2010) Int J Epidemiol Res. 2015;2(4):184–9.
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

