Phosphoserine inhibits neighboring arginine methylation in the RKS motif of histone H3
- PMID: 33309545
- PMCID: PMC11028399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108716
Phosphoserine inhibits neighboring arginine methylation in the RKS motif of histone H3
Abstract
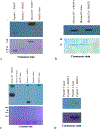
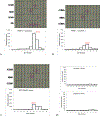
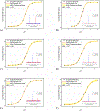
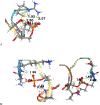
The effects of phosphorylation of histone H3 at serine 10 have been studied in the context of other posttranslational modifications such as lysine methylation. We set out to investigate the impact of phosphoserine-10 on arginine-8 methylation. We performed methylation reactions using peptides based on histone H3 that contain a phosphorylated serine and compared the extent of arginine methylation with unmodified peptides. Results obtained via fluorography indicate that peptides containing a phosphorylated serine-10 inhibit deposition of methyl groups to arginine-8 residues. To further explore the effects of phosphoserine on neighboring arginine residues, we physically characterized the non-covalent interactions between histone H3 phosphoserine-10 and arginine-8 using 31P NMR spectroscopy. A salt bridge was detected between the negatively charged phosphoserine-10 and the positively charged unmodified arginine-8 residue. This salt bridge was not detected when arginine-8 was symmetrically dimethylated. Finally, molecular simulations not only confirm the presence of a salt bridge but also identify a subset of electrostatic interactions present when arginine is replaced with alanine. Taken together, our work suggests that the negatively charged phosphoserine maximizes its interactions. By limiting its exposure and creating new contacts with neighboring residues, it will inhibit deposition of neighboring methyl groups, not through steric hindrance, but by forming intrapeptide interactions that may mask substrate recognition. Our work provides a mechanistic framework for understanding the role of phosphoserine on nearby amino acid residues and arginine methylation.
Keywords: Histone crosstalk; Methylarginine; Methylation; PRMT; Phosphorylation; Phosphoserine; Post translational modification (PTM); Symmetric arginine dimethylation (SDMA).
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson DE, Becktel WJ, & Dahlquist FW (1990). pH-induced denaturation of proteins: a single salt bridge contributes 3–5 kcal/mol to the free energy of folding of T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry, 29(9), 2403–2408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

