Requirement of DNMT1 to orchestrate epigenomic reprogramming for NPM-ALK-driven lymphomagenesis
- PMID: 33310759
- PMCID: PMC7768196
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202000794
Requirement of DNMT1 to orchestrate epigenomic reprogramming for NPM-ALK-driven lymphomagenesis
Abstract
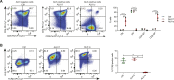
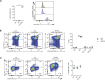
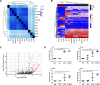
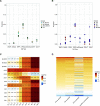
Malignant transformation depends on genetic and epigenetic events that result in a burst of deregulated gene expression and chromatin changes. To dissect the sequence of events in this process, we used a T-cell-specific lymphoma model based on the human oncogenic nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (NPM-ALK) translocation. We find that transformation of T cells shifts thymic cell populations to an undifferentiated immunophenotype, which occurs only after a period of latency, accompanied by induction of the MYC-NOTCH1 axis and deregulation of key epigenetic enzymes. We discover aberrant DNA methylation patterns, overlapping with regulatory regions, plus a high degree of epigenetic heterogeneity between individual tumors. In addition, ALK-positive tumors show a loss of associated methylation patterns of neighboring CpG sites. Notably, deletion of the maintenance DNA methyltransferase DNMT1 completely abrogates lymphomagenesis in this model, despite oncogenic signaling through NPM-ALK, suggesting that faithful maintenance of tumor-specific methylation through DNMT1 is essential for sustained proliferation and tumorigenesis.
© 2020 Redl et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures











References
-
- Zhang Q, Wang HY, Liu X, Bhutani G, Kantekure K, Wasik M (2011) IL-2R common gamma-chain is epigenetically silenced by nucleophosphin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (NPM-ALK) and acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting NPM-ALK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 11977–11982. 10.1073/pnas.1100319108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee H, Zhang P, Herrmann A, Yang C, Xin H, Wang Z, Hoon DS, Forman SJ, Jove R, Riggs AD, et al. (2012) Acetylated STAT3 is crucial for methylation of tumor-suppressor gene promoters and inhibition by resveratrol results in demethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 7765–7769. 10.1073/pnas.1205132109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
