LINC00987 Ameliorates COPD by Regulating LPS-Induced Cell Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Autophagy Through Let-7b-5p/SIRT1 Axis
- PMID: 33311978
- PMCID: PMC7726835
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S276429
LINC00987 Ameliorates COPD by Regulating LPS-Induced Cell Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Autophagy Through Let-7b-5p/SIRT1 Axis
Abstract
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third cause of disease-related death and brings a heavy burden to human health. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) was revealed to participate in COPD pathogenesis. This study aims to establish the effects and regulatory mechanism of lncRNA long intergenic non-coding 00987 (LINC00987) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation and autophagy in BEAS-2B cells.
Methods: The expression levels of LINC00987 and let-7b-5p were detected by real-time quantitativepolymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The expression of apoptosis-associated proteins, oxidative stress (ROS)-related proteins, autophagy-related proteins and sirtuin1 (SIRT1) protein was determined by Western blot. Cell viability was illustrated by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Cell apoptosis was investigated by caspase3 activity and apoptosis analysis assays. ROS, inflammation and autophagy were demonstrated by detecting reactive ROS level and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blot analysis, respectively. The binding sites between let-7b-5p and LINC00987 or SIRT1 were predicted by lncBase or miRWalk online database, and identified by dual-luciferase reporter assay.
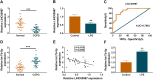
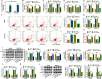
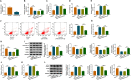
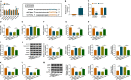
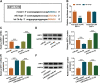
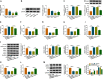
Results: LINC00987 expression was strikingly downregulated and let-7b-5p expression was obviously upregulated in COPD tissues and LPS-induced BEAS-2B cells compared with control groups. LINC00987 overexpression promoted BEAS-2B cells against LPS-mediated viability, apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation and autophagy, whereas these effects were attenuated by let-7b-5p mimic or SIRT1 knockdown. Furthermore, LINC00987 sponged let-7b-5p and let-7b-5p bound to SIRT1.
Conclusion: LINC00987 ameliorated COPD through modulating LPS-induced cell apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation and autophagy via sponging let-7b-5p to associate with SIRT1. This finding will provide a theoretical basis for the research of LncRNA-mediated treatment in COPD.
Keywords: COPD; LINC00987; LPS; SIRT1; let-7b-5p.
© 2020 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or non-financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

