Randomized Prospective Comparison of Glidescope Video Laryngoscope with Macintosh Laryngoscope in Adult who Underwent Thyroid or Parathyroid Surgery Using Neuromonitorization
- PMID: 33312030
- PMCID: PMC7729713
- DOI: 10.14744/SEMB.2020.06887
Randomized Prospective Comparison of Glidescope Video Laryngoscope with Macintosh Laryngoscope in Adult who Underwent Thyroid or Parathyroid Surgery Using Neuromonitorization
Abstract
Objectives: The present study aims to compare the effects of Glidescope Video Laryngoscope (GVL) and Machintosh Laryngoscope (ML) on the hemodynamic response, intubation time and mucosal damage in adult patients who underwent thyroid or parathyroid surgery using neuromonitorization.
Methods: In this study, 180 patients, aged between 22 and 65 classified as Class I-II in ASA (American Society of Anesthesiologists) and operated under elective conditions were included. Patients were assigned into two groups: Patients intubated with GVL Group G (n=90) and patients intubated with ML Group M (n=90). In both groups, intubation time and the number of trials were recorded. HR (Heart Rate), SpO2 (Peripheral Capillary Oxygen Saturation), SBP (Systolic Blood Pressure), DBP (Diastolic Blood Pressure) and MBP (Mean Blood Pressure) scores were recorded at preinduction, post-induction, post-intubation and three minutes after intubation. Post-operative intubation-associated complications were recorded.
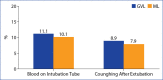
Results: Post intubation HR, DBP and MBP scores were found to be significantly higher in Group M than Group G (p=0,006, p=0.013, p=0.011). Intubation time was found to be significantly higher in Group G than in group M (35.3±10.3, 22.1±7.7 sec). There was no significant difference between the groups' number of trials and intubation-associated complications.
Conclusion: Despite its long intubation time, we believe that GVL may be the first choice laryngoscopy method in the thyroid or parathyroid cases that intubated with a low dose muscle relaxant for neuromonitoring since it has a slight effect than ML on hemodynamism it does not increase mucosal damage and has improved visibility.
Keywords: Glidescope video laryngoscope; macintosh laryngoscope; neuromonitorization; parathyroid surgery; thyroid surgery.
Copyright: © 2019 by The Medical Bulletin of Sisli Etfal Hospital.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Kayhan Z. Klinik Anestezi. 3rd ed. İstanbul: Logos Publishing; 2004. pp. 243–73.
-
- İsgör A. 1st ed. Istanbul: Avrupa Tıp; 2000. Tiroid Hastalıklarıve Cerrahisi; pp. 515–93.
-
- Eisele DW. Intraoperative electrophysiologic monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Laryngoscope. 1996;106:443–49. - PubMed
-
- Han YD, Liang F, Chen P. Dosage effect of rocuronium on intraoperative neuromonitoring in patients undergoing thyroid surgery. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;71:143–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous