Malnutrition in cirrhosis: More food for thought
- PMID: 33312416
- PMCID: PMC7701970
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.883
Malnutrition in cirrhosis: More food for thought
Abstract
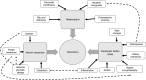
Malnutrition is highly prevalent in liver cirrhosis and its presence carries important prognostic implications. The clinical conditions and pathophysiological mechanisms that cause malnutrition in cirrhosis are multiple and interrelated. Anorexia and liver decompensation symptoms lead to poor dietary intake; metabolic changes characterised by elevated energy expenditure, reduced glycogen storage, an accelerated starvation response and protein catabolism result in muscle and fat wasting; and, malabsorption renders the cirrhotic patient unable to fully absorb or utilise food that has been consumed. Malnutrition is therefore a considerable challenge to manage effectively, particularly as liver disease progresses. A high energy, high protein diet is recognised as standard of care, yet patients struggle to follow this recommendation and there is limited evidence to guide malnutrition interventions in cirrhosis and liver transplantation. In this review, we seek to detail the factors which contribute to poor nutritional status in liver disease, and highlight complexities far greater than "poor appetite" or "reduced oral intake" leading to malnutrition. We also discuss management strategies to optimise nutritional status in this patient group, which target the inter-related mechanisms unique to advanced liver disease. Finally, future research requirements are suggested, to develop effective treatments for one of the most common and debilitating complications afflicting cirrhotic patients.
Keywords: Chronic liver disease; Cirrhosis; Liver transplantation; Malnutrition; Nutrition; Sarcopenia.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson TM, Overgard EB, Cohen AE, DiBaise JK. Nutrition assessment and management in advanced liver disease. Nutr Clin Pract. 2013;28:15–29. - PubMed
-
- Cheung K, Lee SS, Raman M. Prevalence and mechanisms of malnutrition in patients with advanced liver disease, and nutrition management strategies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Tsiaousi ET, Hatzitolios AI, Trygonis SK, Savopoulos CG. Malnutrition in end stage liver disease: recommendations and nutritional support. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:527–533. - PubMed
-
- D'Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006;44:217–231. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Tsao G, Sanyal AJ, Grace ND, Carey W Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2007;46:922–938. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources