Treatment options for aseptic tibial diaphyseal nonunion: A review of selected studies
- PMID: 33312710
- PMCID: PMC7722944
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190077
Treatment options for aseptic tibial diaphyseal nonunion: A review of selected studies
Abstract
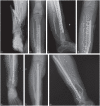
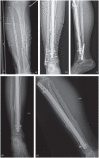
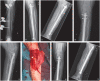
In aseptic tibial diaphyseal nonunions after failed conservative treatment, the recommended treatment is a reamed intramedullary (IM) nail.Typically, when an aseptic tibial nonunion previously treated with an IM nail is found, it is advisable to change the previous IM nail for a larger diameter reamed and locked IM nail (the rate of success of renailing is around 90%).A second change after an IM nail failure is also a good option, especially if bone healing has progressed after the first change.Fibular osteotomy is not routinely advised; it is only recommended when it interferes with the nonunion site.In delayed unions before 24 weeks, IM nail dynamization can be performed as a less invasive option before deciding on a nail change.If there is a bone defect, a bone graft must be recommended, with the gold standard being the autologous iliac crest bone graft (AICBG).A reamer-irrigator-aspirator (RIA) system might also obtain a bone autograft that is comparable to AICBG.Although the size of the bone defect suitable to perform bone transport techniques is a controversial issue, we believe that such techniques can be considered in bone defects > 3 cm.Non-invasive therapies and biologic therapies could be applied in isolation for patients with high surgical risk, or could be used as adjuvants to the aforementioned surgical treatments. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2020;5:835-844. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190077.
Keywords: aseptic nonunion; tibial diaphysis; treatment options.
© 2020 The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest relevant to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Browner B, Jupiter J, Levine A, Trafton P, Krettek C. Skeletal trauma: basic science, management and reconstruction. Fourth ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2009.
-
- Rupp M, Biehl C, Budak M, Thormann U, Heiss C, Alt V. Diaphyseal long bone nonunions: types, aetiology, economics, and treatment recommendations. Int Orthop 2018;42:247–258. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Merchan EC, Forriol F. Nonunion: general principles and experimental data. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004;419:4–12. - PubMed
-
- Kohlprath R, Assal M, Uçkay I, Holzer N, Hoffmeyer P, Suva D. Open fractures of the tibia in the adult: surgical treatment and complications. Rev Med Suisse 2011;7:2482, 2484–2488. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

