Preclinical evaluation of the epithelial sodium channel inhibitor BI 1265162 for treatment of cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 33313305
- PMCID: PMC7720687
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00429-2020
Preclinical evaluation of the epithelial sodium channel inhibitor BI 1265162 for treatment of cystic fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) is an important regulator of airway surface liquid volume; ENaC is hyperactivated in cystic fibrosis (CF). ENaC inhibition is a potential therapeutic target for CF. Here, we report in vitro and in vivo results for BI 1265162, an inhaled ENaC inhibitor currently in Phase II clinical development, administered via the Respimat® Soft Mist™ inhaler.
Methods: In vitro inhibition of sodium ion (Na+) transport by BI 1265162 was tested in mouse renal collecting duct cells (M1) and human bronchial epithelial cells (NCI-H441); inhibition of water transport was measured using M1 cells. In vivo inhibition of liquid absorption from rat airway epithelium and acceleration of mucociliary clearance (MCC) in sheep lungs were assessed. Fully differentiated normal and CF human epithelium was used to measure the effect of BI 1265162 with or without ivacaftor and lumacaftor on water transport and MCC.
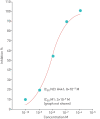
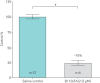
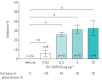
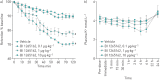
Results: BI 1265162 dose-dependently inhibited Na+ transport and decreased water resorption in cell line models. BI 1265162 reduced liquid absorption in rat lungs and increased MCC in sheep. No effects on renal function were seen in the animal models. BI 1265162 alone and in combination with CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulators decreased water transport and increased MCC in both normal and CF airway human epithelial models and also increased the effects of CFTR modulators in CF epithelium to reach the effect size seen in healthy epithelium with ivacaftor/lumacaftor alone.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate the potential of BI 1265162 as a mutation agnostic, ENaC-inhibitor-based therapy for CF.
Copyright ©ERS 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: P. Nickolaus is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Conflict of interest: B. Jung was an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim at the time of the study. Conflict of interest: J. Sabater reports grants from Boehringer Ingelheim during the conduct of the study. Conflict of interest: S. Constant reports grants from Boehringer Ingelheim during the conduct of the study. Conflict of interest: A. Gupta is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ursodeoxycholic acid inhibits ENaC and Na/K pump activity to restore airway surface liquid height in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells.Steroids. 2019 Nov;151:108461. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2019.108461. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Steroids. 2019. PMID: 31344409
-
Preclinical evaluation of the epithelial sodium channel inhibitor AZD5634 and implications on human translation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022 Nov 1;323(5):L536-L547. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00454.2021. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36098422 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapy of the ion transport defect in cystic fibrosis: role of purinergic receptor agonists and other potential therapeutics.Am J Respir Med. 2003;2(4):299-309. doi: 10.1007/BF03256658. Am J Respir Med. 2003. PMID: 14719996 Review.
-
SPX-101 Is a Novel Epithelial Sodium Channel-targeted Therapeutic for Cystic Fibrosis That Restores Mucus Transport.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 Sep 15;196(6):734-744. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201612-2445OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28481660
-
The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) as a therapeutic target for cystic fibrosis lung disease.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Aug;22(8):687-701. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1501361. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 30028216 Review.
Cited by
-
An innovative phase II trial to establish proof of efficacy and optimal dose of a new inhaled epithelial sodium channel inhibitor BI 1265162 in adults and adolescents with cystic fibrosis: BALANCE-CFTM 1.ERJ Open Res. 2020 Dec 7;6(4):00395-2020. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00395-2020. eCollection 2020 Oct. ERJ Open Res. 2020. PMID: 33313307 Free PMC article.
-
ENaC inhibition in cystic fibrosis: potential role in the new era of CFTR modulator therapies.Eur Respir J. 2020 Dec 24;56(6):2000946. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00946-2020. Print 2020 Dec. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32732328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Pulmonary Disease of Cystic Fibrosis: A Comprehensive Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;10(5):486. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10050486. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of inhaled ENaC inhibitor BI 1265162 in patients with cystic fibrosis: BALANCE-CF 1, a randomised, phase II study.Eur Respir J. 2022 Feb 17;59(2):2100746. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00746-2021. Print 2022 Feb. Eur Respir J. 2022. PMID: 34385272 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacological Modulation of Ion Channels for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis.J Exp Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 23;13:693-723. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S255377. eCollection 2021. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34326672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
