Cervical Sagittal Imbalance after Cervical Laminoplasty in Elderly Patients
- PMID: 33313319
- PMCID: PMC7721504
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8810540
Cervical Sagittal Imbalance after Cervical Laminoplasty in Elderly Patients
Abstract
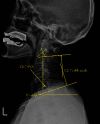
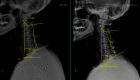
Purpose: To determine the effect of age on sagittal cervical alignment after cervical laminoplasty procedure so as to identify the group with the greatest degree of variation. Study Setting. Single-center retrospective chart review in a tertiary referral hospital. Outcome Measures. The sagittal vertical axis (SVA) (C2-7), T1 slope, and cervical lordosis.
Methods: We included patients who underwent cervical laminoplasty between 2014 and 2018 and divided 60 consecutive patients into two groups using the cut-off age of 65 years. The Paired t-test and Mann-Whitney U test were used to compare changes between preoperative radiographic cervical sagittal parameters and those 1 year after surgery.
Results: Mean patient ages in the older and younger groups were 71 years and 52 years, respectively. The difference of C2-7 SVA was greater in the older group.
Conclusion: Postoperative cervical balance can be worse when laminoplasty is performed in elderly patients.
Copyright © 2020 Hyun Woong Mun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers' bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements) or nonfinancial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Kwon S., Kang S. H., Jeon S. R., Roh S. W., Rhim S. C. Cervical laminoplasty: factors associated with cervical myelopathy. Korean Journal of Spine. 2006;3(4):205–212.
-
- Sakaura H., Ohnishi A., Yamagishi A., Ohwada T. Differences in postoperative changes of cervical sagittal alignment and balance after laminoplasty between cervical spondylotic myelopathy and cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Global Spine Journal. 2019;9(3):266–271. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

