Joint preoperative transthoracic and intraoperative transoesophageal echocardiographic assessment of functional mitral regurgitation severity provides better association with long-term mortality
- PMID: 33313764
- PMCID: PMC8600023
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivaa230
Joint preoperative transthoracic and intraoperative transoesophageal echocardiographic assessment of functional mitral regurgitation severity provides better association with long-term mortality
Abstract
Objectives: Functional mitral regurgitation (MR) is observed with ischaemic heart disease or aortic valve disease. Assessing the value of mitral valve repair or replacement (MVR/P) is complicated by frequent discordance between preoperative transthoracic echocardiographic (pTTE) and intraoperative transoesophageal echocardiographic (iTOE) assessment of MR severity. We examined the association of pTTE and iTOE with postoperative mortality in patients with or without MR, at the time of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and/or aortic valve replacement without MVR/P.
Methods: Medical records of 6629 patients undergoing CABG and/or aortic valve replacement surgery with or without functional MR and who did not undergo MVR/P were reviewed. MR severity assessed by pTTE and iTOE were examined for association with postoperative mortality using proportional hazards regression while accounting for patient and operative characteristics.
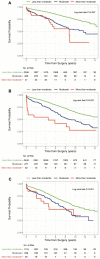
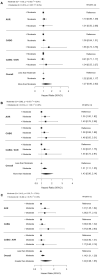
Results: In 72% of 709 patients with clinically significant (moderate or greater) functional MR detected by pTTE, iTOE performed after induction of anaesthesia demonstrated a reduction in MR severity, while 2% of patients had increased severity of MR by iTOE. iTOE assessment of MR was better associated with long-term postoperative mortality than pTTE in patients with moderate MR [hazard ratio (HR) 1.31 (1.11-1.55) vs 1.02 (0.89-1.17), P-value for comparison of HR 0.025] but was not different for more than moderate MR [1.43 (0.96-2.14) vs 1.27 (0.80-2.02)].
Conclusions: In patients undergoing CABG and/or aortic valve replacement without MVR/P, these findings support intraoperative reassessment of MR severity by iTOE as an adjunct to pTTE in the prediction of mortality. Alone, these findings do not yet provide evidence for an operative strategy.
Keywords: Intraoperative transoesophageal echocardiographic; Mitral regurgitation; Preoperative transthoracic echocardiographic.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Enriquez-Sarano M, Akins CW, Vahanian A.. Mitral regurgitation. Lancet 2009;373:1382–94. - PubMed
-
- Alghamdi AA, Elmistekawy EM, Singh SK, Latter DA.. Is concomitant surgery for moderate functional mitral regurgitation indicated during aortic valve replacement for aortic stenosis? A systematic review and evidence-based recommendations. J Card Surg 2010;25:182–7. - PubMed
-
- Penicka M, Linkova H, Lang O, Fojt R, Kocka V, Vanderheyden M. et al. Predictors of improvement of unrepaired moderate ischemic mitral regurgitation in patients undergoing elective isolated coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Circulation 2009;120:1474–81. - PubMed
-
- Harling L, Saso S, Jarral OA, Kourliouros A, Kidher E, Athanasiou T.. Aortic valve replacement for aortic stenosis in patients with concomitant mitral regurgitation: should the mitral valve be dealt with? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2011;40:1087–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

