Urine proteomics for prediction of disease progression in patients with IgA nephropathy
- PMID: 33313853
- PMCID: PMC8719618
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa307
Urine proteomics for prediction of disease progression in patients with IgA nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Risk of kidney function decline in immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy (IgAN) is significant and may not be predicted by available clinical and histological tools. To serve this unmet need, we aimed at developing a urinary biomarker-based algorithm that predicts rapid disease progression in IgAN, thus enabling a personalized risk stratification.
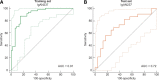
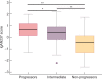
Methods: In this multicentre study, urine samples were collected in 209 patients with biopsy-proven IgAN. Progression was defined by tertiles of the annual change of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) during follow-up. Urine samples were analysed using capillary electrophoresis coupled mass spectrometry. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the risk prediction models.
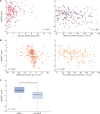
Results: Of the 209 patients, 64% were male. Mean age was 42 years, mean eGFR was 63 mL/min/1.73 m2 and median proteinuria was 1.2 g/day. We identified 237 urine peptides showing significant difference in abundance according to the tertile of eGFR change. These included fragments of apolipoprotein C-III, alpha-1 antitrypsin, different collagens, fibrinogen alpha and beta, titin, haemoglobin subunits, sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit gamma, uromodulin, mucin-2, fractalkine, polymeric Ig receptor and insulin. An algorithm based on these protein fragments (IgAN237) showed a significant added value for the prediction of IgAN progression [AUC 0.89; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.83-0.95], as compared with the clinical parameters (age, gender, proteinuria, eGFR and mean arterial pressure) alone (0.72; 95% CI 0.64-0.81).
Conclusions: A urinary peptide classifier predicts progressive loss of kidney function in patients with IgAN significantly better than clinical parameters alone.
Keywords: IgAN; biomarker; glomerulonephritis; progression; urine proteomics.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures


References
-
- McGrogan A, Franssen CF, de Vries CS. The incidence of primary glomerulonephritis worldwide: a systematic review of the literature. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2011; 26: 414–430 - PubMed
-
- Barbour SJ, Espino-Hernandez G, Reich HN et al. . The MEST score provides earlier risk prediction in lgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 2016; 89: 167–175 - PubMed
-
- Reich HN, Troyanov S, Scholey JW et al. . Remission of proteinuria improves prognosis in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007; 18: 3177–3183 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

