Upadacitinib monotherapy improves patient-reported outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis: results from SELECT-EARLY and SELECT-MONOTHERAPY
- PMID: 33313898
- PMCID: PMC8516509
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa770
Upadacitinib monotherapy improves patient-reported outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis: results from SELECT-EARLY and SELECT-MONOTHERAPY
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of upadacitinib (UPA) monotherapy vs MTX on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in patients with RA who were MTX-naïve or who had an inadequate response to MTX (MTX-IR).
Methods: PROs from the SELECT-EARLY and SELECT-MONOTHERAPY randomized controlled trials were evaluated at Weeks 2 and 12/14. Patients were ≥18 years of age with RA symptoms for ≥6 weeks (SELECT-EARLY, MTX-naïve) or diagnosed RA for ≥3 months (SELECT-MONOTHERAPY, MTX-IR) and received UPA monotherapy (15 or 30 mg) or MTX. PROs included Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity (PtGA), pain visual analogue scale, HAQ Disability Index (HAQ-DI), morning stiffness duration/severity, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue (SELECT-EARLY), health-related quality of life (HRQOL) by the 36-iem Short Form Health Survey and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI; SELECT-EARLY). Least square mean (LSM) changes and proportions of patients reporting improvements greater than or equal to the minimum clinically important differences and normative values were determined.
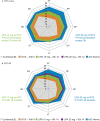
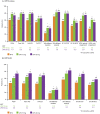
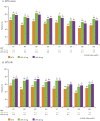
Results: In 945 MTX-naïve and 648 MTX-IR patients, UPA monotherapy (15 mg, 30 mg) vs MTX resulted in greater reported LSM changes from baseline at Weeks 12/14 in PtGA, pain, HAQ-DI, morning stiffness duration/severity, FACIT-F (SELECT-EARLY), HRQOL and WPAI (SELECT-EARLY). These changes were statistically significant with both doses of UPA vs MTX at Weeks 12/14 in both RCTs. Improvements were reported as early as week 2. Compared with MTX, more UPA-treated MTX-naïve and MTX-IR patients reported improvements greater than or equal to the minimum clinically important differences and scores greater than or equal to normative values.
Conclusion: Among MTX-naïve and MTX-IR patients with active RA, UPA monotherapy at 15 or 30 mg for 12/14 weeks resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pain, physical function, morning stiffness, HRQOL and WPAI compared with MTX alone.
Clinical trial registration number: SELECT-EARLY (NCT02706873) and SELECT-MONOTHERAPY (NCT02706951) are registered with ClinicalTrials.gov.
Keywords: DMARDs; RA; inflammation; outcome measures; quality of life.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB.. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016;388:2023–38. - PubMed
-
- Strand V, Khanna D.. The impact of rheumatoid arthritis and treatment on patients’ lives. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2010;28(3 Suppl 59):S32–40. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe RBM, Bijlsma JWJ. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:685–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

