The role of neuraminidase in TLR4-MAPK signalling and the release of cytokines by lupus serum-stimulated mesangial cells
- PMID: 33314123
- PMCID: PMC7968401
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.13294
The role of neuraminidase in TLR4-MAPK signalling and the release of cytokines by lupus serum-stimulated mesangial cells
Abstract
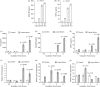
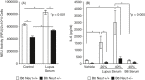
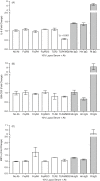
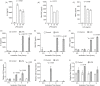
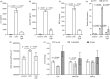
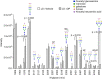
Previously, we demonstrated neuraminidase (NEU) activity or NEU1 expression, specifically, is increased in the kidneys of lupus mice and urine of human patients with nephritis. Additionally, NEU activity mediates IL-6 secretion from lupus-prone MRL/lpr primary mouse mesangial cells (MCs) in response to an IgG mimic. IL-6 mediates glomerular inflammation and promotes tissue damage in patients and mouse strains with lupus nephritis. This study further elucidates the mechanisms by which NEU activity and NEU1 specifically mediates the release of IL-6 and other cytokines from lupus-prone MCs. We demonstrate significantly increased release of multiple cytokines and NEU activity in MRL/lpr MCs in response to serum from MRL/lpr mice (lupus serum). Inhibiting NEU activity significantly reduced secretion of three of those cytokines: IL-6, GM-CSF and MIP1α. Message levels of Il-6 and Gm-csf were also increased in response to lupus serum and reduced when NEU activity was inhibited. Neutralizing antibodies to cell-surface receptors and MAPK inhibitors in lupus serum- or LPS-stimulated MCs indicate TLR4 and p38 or ERK MAP kinase signalling play key roles in the NEU-mediated secretion of IL-6. Significantly reduced IL-6 release was observed in C57BL/6 (B6) Neu1+/+ primary MCs compared with wild-type (Neu1+/+) B6 MCs in response to lupus serum. Additional results show inhibiting NEU activity significantly increases sialic acid-containing N-glycan levels. Together, our novel observations support a role for NEU activity, and specifically NEU1, in mediating release of IL-6 from lupus-prone MCs in response to lupus serum through a TLR4-p38/ERK MAPK signalling pathway that likely includes desialylation of glycoproteins.
Keywords: Toll-like receptor 4; interleukin-6; lupus; mesangial cell; mitogen-activated protein kinase; neuraminidase.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Nitta T, Kanoh H, Inamori KI, Suzuki A, Takahashi T, Inokuchi JI. Globo‐series glycosphingolipids enhance Toll‐like receptor 4‐mediated inflammation and play a pathophysiological role in diabetic nephropathy. Glycobiology. 2019;29:260–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

