Healthy lifestyle behaviors are major predictors of mental wellbeing during COVID-19 pandemic confinement: A study on adult Arabs in higher educational institutions
- PMID: 33315880
- PMCID: PMC7735567
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243524
Healthy lifestyle behaviors are major predictors of mental wellbeing during COVID-19 pandemic confinement: A study on adult Arabs in higher educational institutions
Erratum in
-
Correction: Healthy lifestyle behaviors are major predictors of mental wellbeing during COVID-19 pandemic confinement: A study on adult Arabs in higher educational institutions.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 15;17(8):e0273276. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273276. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35969585 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Healthy lifestyle behaviors are major predictors of mental wellbeing during COVID-19 pandemic confinement: A study on adult Arabs in higher educational institutions.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 30;19(12):e0316869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316869. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39775629 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: In the past infectious diseases affected the quality of lifestyle during home confinement. The study conducted examines the influence of home confinement during the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak on lifestyle, mental wellbeing, nutritional status, and sleeping pattern.
Method: An online multicategorical questionnaire was distributed to collect demographic information combined with the following tools: Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ), International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ), WHO-5 wellbeing score, and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). A snowball non-discriminate sampling procedure was conducted to collect data from people attending or working at higher institutions from March 1, 2020 to April 24, 2020. A total of 1723 completed responses (917 males, 37.4 ±13.4 years old and 806 females 32.2 ± 11.5 years old) were collected.
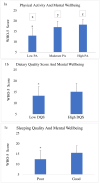
Results: The female participants had significantly lower mental health scores than males (53.9% vs. 46.1%). The mental wellbeing scores were higher among participants with medium and high physical activity (PA) levels (p < 0.00). Additionally, the mental wellbeing scores were significantly improved by dietary quality and it's sleeping score (p < 0.001). However, PA was by far the major determinant of the mental health scores.
Conclusion: Factors such as PA, diet, and sleeping patterns were associated with mental wellbeing during the COVID-19 confinement among Arab participants.
Conflict of interest statement
MH is an employee of Actness. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
-
- The WHO Just Declared Coronavirus COVID-19 a Pandemic. Time [Internet]. https://time.com/5791661/who-coronavirus-pandemicdeclaration/. [cited This preprint research paper has not been peer reviewed. Electronic copy. https://ssrn.com/abstract=3561265 22 2020, Mar 12].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

