Phase-specific manipulation of neuronal activity: a promising stroke therapy approach
- PMID: 33318438
- PMCID: PMC8284296
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.301005
Phase-specific manipulation of neuronal activity: a promising stroke therapy approach
Conflict of interest statement
None
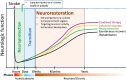
Figures
References
-
- Cramer SC, Wolf SL, Adams HP, Jr, Chen D, Dromerick AW, Dunning K, Ellerbe C, Grande A, Janis S, Lansberg MG, Lazar RM, Palesch YY, Richards L, Roth E, Savitz SI, Wechsler LR, Wintermark M, Broderick JP. Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Research: Issues, Opportunities, and the National Institutes of Health StrokeNet. Stroke. 2017;48:813–819. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hartings JA, Shuttleworth CW, Kirov SA, Ayata C, Hinzman JM, Foreman B, Andrew RD, Boutelle MG, Brennan KC, Carlson AP, Dahlem MA, Drenckhahn C, Dohmen C, Fabricius M, Farkas E, Feuerstein D, Graf R, Helbok R, Lauritzen M, Major S, et al. The continuum of spreading depolarizations in acute cortical lesion development: Examining Leao’s legacy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37:1571–1594. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu KH, Li YA, Jia W, Wu GY, Sun L, Wang SR, Yu LH. Chemogenetic activation of glutamatergic neurons in the motor cortex promotes functional recovery after ischemic stroke in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2019;359:81–88. - PubMed
-
- Mestre H, Du T, Sweeney AM, Liu G, Samson AJ, Peng W, Mortensen KN, Stæger FF, Bork PAR, Bashford L, Toro ER, Tithof J, Kelley DH, Thomas JH, Hjorth PG, Martens EA, Mehta RI, Solis O, Blinder P, Kleinfeld D, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid influx drives acute ischemic tissue swelling. Science. 2020;367:eaax7171. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

