Circulating BMP9 Protects the Pulmonary Endothelium during Inflammation-induced Lung Injury in Mice
- PMID: 33320799
- PMCID: PMC8456542
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1761OC
Circulating BMP9 Protects the Pulmonary Endothelium during Inflammation-induced Lung Injury in Mice
Abstract
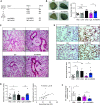
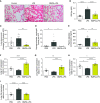
Rationale: Pulmonary endothelial permeability contributes to the high-permeability pulmonary edema that characterizes acute respiratory distress syndrome. Circulating BMP9 (bone morphogenetic protein 9) is emerging as an important regulator of pulmonary vascular homeostasis. Objectives:To determine whether endogenous BMP9 plays a role in preserving pulmonary endothelial integrity and whether loss of endogenous BMP9 occurs during LPS challenge. Methods: A BMP9-neutralizing antibody was administrated to healthy adult mice, and lung vasculature was examined. Potential mechanisms were delineated by transcript analysis in human lung endothelial cells. The impact of BMP9 administration was evaluated in a murine acute lung injury model induced by inhaled LPS. Levels of BMP9 were measured in plasma from patients with sepsis and from endotoxemic mice. Measurements and Main Results: Subacute neutralization of endogenous BMP9 in mice (N = 12) resulted in increased lung vascular permeability (P = 0.022), interstitial edema (P = 0.0047), and neutrophil extravasation (P = 0.029) compared with IgG control treatment (N = 6). In pulmonary endothelial cells, BMP9 regulated transcriptome pathways implicated in vascular permeability and cell-membrane integrity. Augmentation of BMP9 signaling in mice (N = 8) prevented inhaled LPS-induced lung injury (P = 0.0027) and edema (P < 0.0001). In endotoxemic mice (N = 12), endogenous circulating BMP9 concentrations were markedly reduced, the causes of which include a transient reduction in hepatic BMP9 mRNA expression and increased elastase activity in plasma. In human patients with sepsis (N = 10), circulating concentratons of BMP9 were also markedly reduced (P < 0.0001). Conclusions: Endogenous circulating BMP9 is a pulmonary endothelial-protective factor, downregulated during inflammation. Exogenous BMP9 offers a potential therapy to prevent increased pulmonary endothelial permeability in lung injury.
Keywords: BMP signaling in endothelial cells; BMP9; lung injury; pulmonary endothelium.
Figures



Comment in
-
BMP9 in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Decades of BMP Studies in Vascular Biology Paying Off?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Jun 1;203(11):1341-1342. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202012-4388ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33357019 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Millar FR, Summers C, Griffiths MJ, Toshner MR, Proudfoot AG. The pulmonary endothelium in acute respiratory distress syndrome: insights and therapeutic opportunities. Thorax . 2016;71:462–473. - PubMed
-
- David L, Mallet C, Mazerbourg S, Feige JJ, Bailly S. Identification of BMP9 and BMP10 as functional activators of the orphan activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) in endothelial cells. Blood . 2007;109:1953–1961. - PubMed
-
- Scharpfenecker M, van Dinther M, Liu Z, van Bezooijen RL, Zhao Q, Pukac L, et al. BMP-9 signals via ALK1 and inhibits bFGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation and VEGF-stimulated angiogenesis. J Cell Sci . 2007;120:964–972. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL108801/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/19/3/34265/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/17/1/32532/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/14/62/31034/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/17/58/33134/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/15/39/31519/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL159443/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K020919/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/13/4/30107/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/12/54/29734/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R42 HL132742/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- FS/18/40/33650/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

