Transcriptome analysis of sevoflurane exposure effects at the different brain regions
- PMID: 33320849
- PMCID: PMC7737892
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236771
Transcriptome analysis of sevoflurane exposure effects at the different brain regions
Abstract
Backgrounds: Sevoflurane is a most frequently used volatile anesthetics, but its molecular mechanisms of action remain unclear. We hypothesized that specific genes play regulatory roles in brain exposed to sevoflurane. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the effects of sevoflurane inhalation and identify potential regulatory genes by RNA-seq analysis.
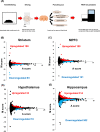
Methods: Eight-week old mice were exposed to sevoflurane. RNA from medial prefrontal cortex, striatum, hypothalamus, and hippocampus were analysed using RNA-seq. Differently expressed genes were extracted and their gene ontology terms were analysed using Metascape. These our anesthetized mouse data and the transcriptome array data of the cerebral cortex of sleeping mice were compared. Finally, the activities of transcription factors were evaluated using a weighted parametric gene set analysis (wPGSA). JASPAR was used to confirm the existence of binding motifs in the upstream sequences of the differently expressed genes.
Results: The gene ontology term enrichment analysis result suggests that sevoflurane inhalation upregulated angiogenesis and downregulated neural differentiation in each region of brain. The comparison with the brains of sleeping mice showed that the gene expression changes were specific to anesthetized mice. Focusing on individual genes, sevoflurane induced Klf4 upregulation in all sampled parts of brain. wPGSA supported the function of KLF4 as a transcription factor, and KLF4-binding motifs were present in many regulatory regions of the differentially expressed genes.
Conclusions: Klf4 was upregulated by sevoflurane inhalation in the mouse brain. The roles of KLF4 might be key to elucidating the mechanisms of sevoflurane induced functional modification in the brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

