Optimised genetic algorithm-extreme learning machine approach for automatic COVID-19 detection
- PMID: 33320858
- PMCID: PMC7737907
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242899
Optimised genetic algorithm-extreme learning machine approach for automatic COVID-19 detection
Abstract
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19), is an ongoing global pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome. Chest Computed Tomography (CT) is an effective method for detecting lung illnesses, including COVID-19. However, the CT scan is expensive and time-consuming. Therefore, this work focus on detecting COVID-19 using chest X-ray images because it is widely available, faster, and cheaper than CT scan. Many machine learning approaches such as Deep Learning, Neural Network, and Support Vector Machine; have used X-ray for detecting the COVID-19. Although the performance of those approaches is acceptable in terms of accuracy, however, they require high computational time and more memory space. Therefore, this work employs an Optimised Genetic Algorithm-Extreme Learning Machine (OGA-ELM) with three selection criteria (i.e., random, K-tournament, and roulette wheel) to detect COVID-19 using X-ray images. The most crucial strength factors of the Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) are: (i) high capability of the ELM in avoiding overfitting; (ii) its usability on binary and multi-type classifiers; and (iii) ELM could work as a kernel-based support vector machine with a structure of a neural network. These advantages make the ELM efficient in achieving an excellent learning performance. ELMs have successfully been applied in many domains, including medical domains such as breast cancer detection, pathological brain detection, and ductal carcinoma in situ detection, but not yet tested on detecting COVID-19. Hence, this work aims to identify the effectiveness of employing OGA-ELM in detecting COVID-19 using chest X-ray images. In order to reduce the dimensionality of a histogram oriented gradient features, we use principal component analysis. The performance of OGA-ELM is evaluated on a benchmark dataset containing 188 chest X-ray images with two classes: a healthy and a COVID-19 infected. The experimental result shows that the OGA-ELM achieves 100.00% accuracy with fast computation time. This demonstrates that OGA-ELM is an efficient method for COVID-19 detecting using chest X-ray images.
Conflict of interest statement
NO authors have competing interests.
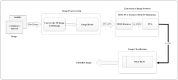
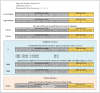
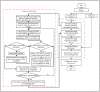
Figures




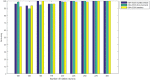
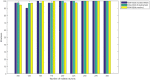
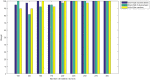
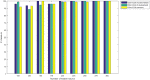
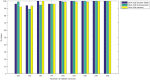
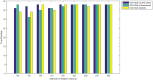
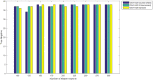
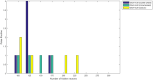
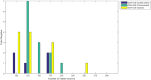
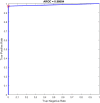
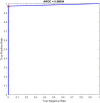
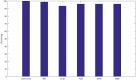
References
-
- Gozes O, Frid-Adar M, Greenspan H, Browning PD, Zhang H, Ji W, et al. (2020) Rapid ai development cycle for the coronavirus (covid-19) pandemic: Initial results for automated detection & patient monitoring using deep learning ct image analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:200305037.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

