Ischemic Stroke in Patients with COVID-19 Disease: A Report of 10 Cases from Iran
- PMID: 33321492
- PMCID: PMC7801957
- DOI: 10.1159/000513279
Ischemic Stroke in Patients with COVID-19 Disease: A Report of 10 Cases from Iran
Abstract
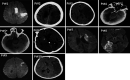
Ischemic stroke seems to be one of the most serious neurologic complications in patients with COVID-19 infection. Herein, we report a series of 10 ischemic stroke patients with concomitant COVID-19 disease. Out of 10, 8 had large infarcts (3 massive middle cerebral artery, 2 basilar artery, 2 posterior cerebral artery, and 1 internal carotid artery infarct territory). Two had cardiogenic embolic stroke due to atrial fibrillation. Almost half of our patients did not have a vascular risk factor. Nine did not have fever and were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon admission for stroke. Stroke occurred in the first week of respiratory symptoms with moderate pulmonary involvement. Most Patients did not have hypoxia and did not establish respiratory failure or acute respiratory distress syndrome. The blood pressures were low and hemorrhagic transformation did not occur even after antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy. Patients had markedly increased levels of lactate dehydrogenase, C-reactive protein, and D-dimer. Three patients died. It seems that ischemic strokes in COVID-19 patients tend to occur as large infarct and can be seen in patients with mild to moderate pulmonary involvement.
Keywords: COVID-19; Case series study; Cerebrovascular diseases; Coronavirus; Ischemic stroke; Neurological manifestations.
© 2020 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Desforges M, Favreau DJ, Brison É, Desjardins J, Meessen-Pinard M, Jacomy H, et al. Human coronaviruses: respiratory pathogens revisited as infectious neuroinvasive, neurotropic, and neurovirulent agents. 2013.
-
- Mao L, Wang M, Chen S, He Q, Chang J, Hong C, et al. Neurological manifestations of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective case series study. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials