RNAi Mediated Hypoxia Stress Tolerance in Plants
- PMID: 33321742
- PMCID: PMC7764064
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249394
RNAi Mediated Hypoxia Stress Tolerance in Plants
Abstract
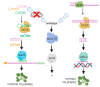
Small RNAs regulate various biological process involved in genome stability, development, and adaptive responses to biotic or abiotic stresses. Small RNAs include microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are regulators of gene expression that affect the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation in plants and animals through RNA interference (RNAi). miRNAs are endogenous small RNAs that originate from the processing of non-coding primary miRNA transcripts folding into hairpin-like structures. The mature miRNAs are incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and drive the Argonaute (AGO) proteins towards their mRNA targets. siRNAs are generated from a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) of cellular or exogenous origin. siRNAs are also involved in the adaptive response to biotic or abiotic stresses. The response of plants to hypoxia includes a genome-wide transcription reprogramming. However, little is known about the involvement of RNA signaling in gene regulation under low oxygen availability. Interestingly, miRNAs have been shown to play a role in the responses to hypoxia in animals, and recent evidence suggests that hypoxia modulates the expression of various miRNAs in plant systems. In this review, we describe recent discoveries on the impact of RNAi on plant responses to hypoxic stress in plants.
Keywords: RNAi; argonaute; hypoxia; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

