Synthetic Methods of Phosphonopeptides
- PMID: 33322827
- PMCID: PMC7764405
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25245894
Synthetic Methods of Phosphonopeptides
Abstract
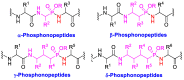
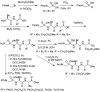
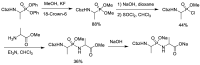
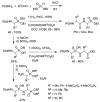
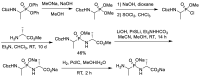
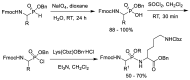
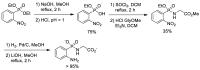
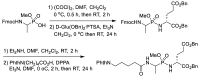
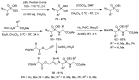
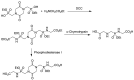
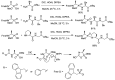
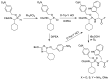
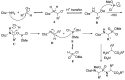
Phosphonopeptides are phosphorus analogues of peptides and have been widely applied as enzyme inhibitors and antigens to induce catalytic antibodies. Phosphonopeptides generally contain one aminoalkylphosphonic acid residue and include phosphonopeptides with C-terminal aminoalkylphosphonic acids and phosphonopeptides with a phosphonamidate bond. The phosphonamidate bond in the phosphonopeptides is generally formed via phosphonylation with phosphonochloridates, condensation with coupling reagents and enzymes, and phosphinylation followed by oxidation. Pseudo four-component condensation reaction of amides, aldehydes, alkyl dichlorophosphites, and amino/peptide esters is an alternative, convergent, and efficient strategy for synthesis of phosphonopeptides through simultaneous construction of aminoalkylphosphonic acids and formation of the phosphonamidate bond. This review focuses on the synthetic methods of phosphonopeptides containing a phosphonamidate bond.
Keywords: peptide; phosphonamidate; phosphonopeptide; β-phosphonopeptide; γ-phosphonopeptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
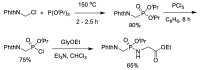
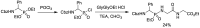
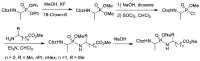
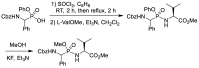


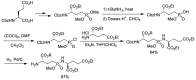
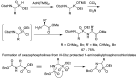
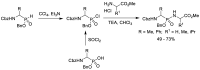
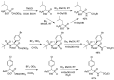
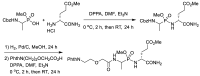
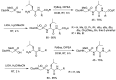
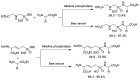
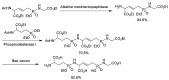
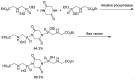
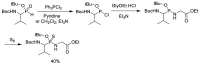
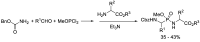
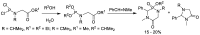
References
-
- Kafarski P., Lejczak B. In: Synthesis of Phosphono- and Phosphinopeptides in Aminophosphonic and Aminophosphinic Acids. Kukhar V.P., Hudson H.R., editors. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; West Sussex, UK: 2000. pp. 173–203.
-
- Kafarski P., Lejczak B. In: The Biological Activity of Phosphono- and Phosphinopeptides in Aminophosphonic and Aminophosphinic Acids. Kukhar V.P., Hudson H.R., editors. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; West Sussex, UK: 2000. pp. 407–442.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

