Implications of Metastable Nicks and Nicked Holliday Junctions in Processing Joint Molecules in Mitosis and Meiosis
- PMID: 33322845
- PMCID: PMC7763299
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11121498
Implications of Metastable Nicks and Nicked Holliday Junctions in Processing Joint Molecules in Mitosis and Meiosis
Abstract
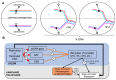
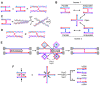
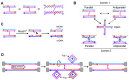
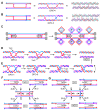
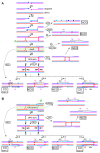
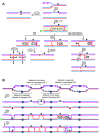
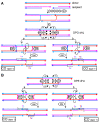
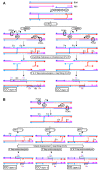
Joint molecules (JMs) are intermediates of homologous recombination (HR). JMs rejoin sister or homolog chromosomes and must be removed timely to allow segregation in anaphase. Current models pinpoint Holliday junctions (HJs) as a central JM. The canonical HJ (cHJ) is a four-way DNA that needs specialized nucleases, a.k.a. resolvases, to resolve into two DNA molecules. Alternatively, a helicase-topoisomerase complex can deal with pairs of cHJs in the dissolution pathway. Aside from cHJs, HJs with a nick at the junction (nicked HJ; nHJ) can be found in vivo and are extremely good substrates for resolvases in vitro. Despite these findings, nHJs have been neglected as intermediates in HR models. Here, I present a conceptual study on the implications of nicks and nHJs in the final steps of HR. I address this from a biophysical, biochemical, topological, and genetic point of view. My conclusion is that they ease the elimination of JMs while giving genetic directionality to the final products. Additionally, I present an alternative view of the dissolution pathway since the nHJ that results from the second end capture predicts a cross-join isomerization. Finally, I propose that this isomerization nicely explains the strict crossover preference observed in synaptonemal-stabilized JMs in meiosis.
Keywords: BLM/Sgs1; GEN1/Yen1; Mlh1-Mlh3/MutLγ; Mus81; ZMM pathway; dissolution pathway; double strand breaks; holliday junction; homologous recombination; replication stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Meiotic recombination intermediates are resolved with minimal crossover formation during return-to-growth, an analogue of the mitotic cell cycle.PLoS Genet. 2011 May;7(5):e1002083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002083. Epub 2011 May 26. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21637791 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of single and double Holliday junction recombination intermediates by GEN1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 17;114(3):443-450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1619790114. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28049850 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mlh1-Mlh3 heterodimer is an endonuclease that preferentially binds to Holliday junctions.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 28;289(9):5674-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.533810. Epub 2014 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24443562 Free PMC article.
-
Holliday junction resolution: regulation in space and time.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 Jul;19(100):176-81. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.03.013. Epub 2014 Apr 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24767945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Holliday junction processing enzymes as guardians of genome stability.Trends Biochem Sci. 2014 Sep;39(9):409-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014. PMID: 25131815 Review.
Cited by
-
The Cdc14 Phosphatase Controls Resolution of Recombination Intermediates and Crossover Formation during Meiosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9811. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189811. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575966 Free PMC article.
-
Classical and novel properties of Holliday junction resolvase SynRuvC from Synechocystis sp. PCC6803.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 18;15:1362880. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1362880. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38699476 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous Recombination Subpathways: A Tangle to Resolve.Front Genet. 2021 Aug 2;12:723847. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.723847. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34408777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NCAPH Stabilizes GEN1 in Chromatin to Resolve Ultra-Fine DNA Bridges and Maintain Chromosome Stability.Mol Cells. 2022 Nov 30;45(11):792-805. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2022.0048. Mol Cells. 2022. PMID: 36380731 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical and novel non-canonical activities of the Holliday junction resolvase Yen1.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 11;50(1):259-280. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1225. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34928393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watt P.M., Louis E.J., Borts R.H., Hickson I.D. Sgs1: A eukaryotic homolog of E. coli RecQ that interacts with topoisomerase II in vivo and is required for faithful chromosome segregation. Cell. 1995;81:253–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

