Financial Burden of Atopic Dermatitis Out-of-Pocket Health Care Expenses in the United States
- PMID: 33323748
- PMCID: PMC8560145
- DOI: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000715
Financial Burden of Atopic Dermatitis Out-of-Pocket Health Care Expenses in the United States
Abstract
Background: Atopic dermatitis (AD) is associated with considerable financial cost. However, the full burden of out-of-pocket (OOP) expenses is not well understood.
Objective: We sought to characterize the OOP health care expenses associated with AD management.
Methods: A 25-question voluntary online survey was administered to National Eczema Association members worldwide (n = 113,502). Inclusion criteria (US residents age ≥18 years who either self-reported had AD or were primary caregivers of individuals with AD) were met by 77.3% (1118/1447) of respondents.
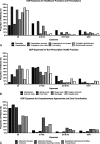
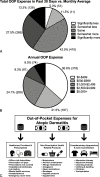
Results: Respondents reported OOP expenses in 3 categories: (1) health care providers and prescriptions, including health care provider visit deductibles (68.7% [686]), prescription co-pays (64.3% [635]), and prescriptions not covered by insurance (48.6% [468]); (2) nonprescription health care products, including moisturizers (94.3% [934]), hygiene products (85.0% [824], allergy medications (75.1% [715]), itch relievers (68.25% [647]), dietary supplements (52.2% [491]), and sleep aids (37.0% [336]); and (3) complementary approaches, including cleaning products (74.7% [732]), clothing/bedding (44.8% [430]), alternative medications (19.0% [180]), and adjunctive therapies (15.9% [150]). The median annual AD OOP expense was US $600 (range, US $0-$200,000), with 41.9% (364) reporting expenditures US $1000 or greater.
Conclusions: Out-of-pocket expenses place a significant financial burden on individuals with AD. Additional studies are needed to better understand associations and impact of OOP costs.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
Conflict of interest statement
R.C. reports personal fees from Abbvie and RegeneronSanofi. J.S. reports personal fees from Abbvie, Anaptysbio, Asana, EliLilly, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, Kiniksa, Leo, Menlo, Pfizer, Realm, RegeneronSanofi, and Roivant, and grants from GlaxoSmithKline, RegeneronSanofi, and Galderma. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Response Letter to the Editor: Impact and Associations of Atopic Dermatitis Out-of-Pocket Health Care Expenses in the United States.Dermatitis. 2022 Nov-Dec 01;33(6S):S145-S146. doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000875. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Dermatitis. 2022. PMID: 35318976 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hua T, Silverberg JI. Atopic dermatitis in US adults: epidemiology, association with marital status, and atopy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2018;121(5):622–624. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg JI Gelfand JM Margolis DJ, et al. . Patient burden and quality of life in atopic dermatitis in US adults: a population-based cross-sectional study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2018;121(3):340–347. - PubMed
-
- Dawn A Papoiu AD Chan YH, et al. . Itch characteristics in atopic dermatitis: results of a web-based questionnaire. Br J Dermatol 2009;160(3):642–644. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg JI Gelfand JM Margolis DJ, et al. . Pain is a common and burdensome symptom of atopic dermatitis in United States adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2019;7:2699–2706.e7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
