Mechanisms and biomarkers of inflammatory endotypes in chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps
- PMID: 33326802
- PMCID: PMC8216505
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.11.037
Mechanisms and biomarkers of inflammatory endotypes in chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps
Abstract
Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) without nasal polyps (CRSsNP) is a common disease that is characterized by multiple inflammatory endotypes. However, the molecular mechanisms in CRSsNP are poorly understood compared with those of polypoid CRS.
Objective: Our aim was to identify mechanisms and biomarkers associated with inflammatory endotypes underpinning CRSsNP.
Methods: Ethmoid tissues and nasal lavage fluids (NLFs) were obtained from control patients and patients with CRS. The gene expression profiles were determined by microarray analysis and quantitative RT-PCR, and expression of proteins was measured by ELISA and Luminex analysis.
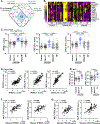
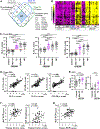
Results: Microarray found that compared with their levels of expression in control tissue, the levels of expression of 126, 241, and 545 genes were more than 3-fold and significantly elevated in CRSsNP with type 1 (T1) endotype, type 2 (T2) endotype, and type 3 (T3) endotype, respectively. Selected identified genes were confirmed by RT-PCR. Gene set enrichment analysis suggested that T1 CRSsNP was associated with IFN-γ signaling and antiviral immunity controlled by T cells (TH1 and CD8+), natural killer cells, and antigen-presenting cells; T2 CRSsNP was associated with STAT6 signaling and IgE-mediated activation controlled by eosinophils, mast cells, TH2 cells, group 2 innate lymphoid cells, and antigen-presenting cells; and T3 CRSsNP was associated with IL-17 signaling, acute inflammatory response, complement-mediated inflammation, and infection controlled by neutrophils, TH17 cells, B cells, and antigen-presenting cells. The results suggest that T1 (CXCL9 and CXCL10), T2 (eosinophilic proteins and CCL26), and T3 (CSF3) endotypic biomarkers in NLF may be able to distinguish tissue endotypes in CRSsNP.
Conclusions: Inflammatory endotypes in CRSsNP were controlled by different molecular mechanisms. NLF biomarker assays may allow for more precise and personalized medical treatments in CRS.
Keywords: Chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps; biomarker; endotype; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2020 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinol Suppl 2012; 23:3 p preceding table of contents, 1–298. - PubMed
-
- Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Hwang PH, Smith TL, Alt JA, Baroody FM, et al. International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology: Rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2016; 6 Suppl 1:S22–209. - PubMed
-
- Smith KA, Orlandi RR, Rudmik L. Cost of adult chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2015; 125:1547–56. - PubMed
-
- Tomassen P, Vandeplas G, Van Zele T, Cardell LO, Arebro J, Olze H, et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016; 137:1449–56 e4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

