Evaluation of Resistance to Fescue Toxicosis in Purebred Angus Cattle Utilizing Animal Performance and Cytokine Response
- PMID: 33327425
- PMCID: PMC7764894
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12120796
Evaluation of Resistance to Fescue Toxicosis in Purebred Angus Cattle Utilizing Animal Performance and Cytokine Response
Abstract
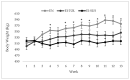
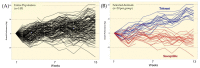
Fescue toxicosis is a multifaceted syndrome common in cattle grazing endophyte-infected tall fescue; however, varying symptomatic responses potentially imply genetic tolerance to the syndrome. It was hypothesized that a subpopulation of animals within a herd would develop tolerance to ergot alkaloid toxicity. Therefore, the goals of this study were to develop selection criteria to identify tolerant and susceptible animals within a herd based on animal performance, and then examine responsive phenotypic and cytokine profiles to fescue toxicosis. Angus cows grazed endophyte-infected tall fescue at two locations for 13 weeks starting in mid-April 2016. Forage measurements were collected to evaluate ergot alkaloid exposure during the study. A post hoc analysis of animal performance was utilized to designate cattle into either tolerant or susceptible groups, and weekly physiological measurements and blood samples were collected to evaluate responses to chronic exposure to endophyte-infected tall fescue. Findings from this study support the proposed fescue toxicosis selection method formulated herein, could accurately distinguish between tolerant and susceptible animals based on the performance parameters in cattle chronically exposed to ergot alkaloids, and provides evidence to warrant additional analysis to examine the impact of ergot alkaloids on immune responsiveness in cattle experiencing fescue toxicosis.
Keywords: cow productivity; cytokines; fescue toxicosis; genetic tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kim J.H., Kim C.W., Ahn G.C., Park E.K., Kim C.M., Park K.K. Ergovaline levels in tall fescue and its effect on performance of lactating cows. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2007;136:330–337. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2007.01.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

