Production, purification and biochemical characterisation of a novel lipase from a newly identified lipolytic bacterium Staphylococcus caprae NCU S6
- PMID: 33327795
- PMCID: PMC7751408
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1861607
Production, purification and biochemical characterisation of a novel lipase from a newly identified lipolytic bacterium Staphylococcus caprae NCU S6
Abstract
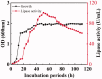
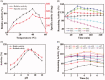
A novel lipase, SCNL, was isolated from Staphylococcus caprae NCU S6 strain in the study. The lipase was purified to homogeneity with a yield of 6.13% and specific activity of 502.76 U/mg, and its molecular weight was determined to be approximately 87 kDa. SCNL maintained above 80% of its initial activity at a wide range of temperatures (20-50 °C) and pH values (6-11), with an optimal temperature at 40 °C and optimal pH at 9.0 with p-nitrophenyl palmitate as a substrate. SCNL exhibited a higher residual activity than the other staphylococcal lipases in the presence of common enzyme inhibitors and commercial detergents. The lipase activity was enhanced by organic solvents (isooctane, glycerol, DMSO and methanol) and metal ions (Na+, Ba2+, Ca2+, and Mn2+). The Km and Vmax values of SCNL were 0.695 mM and 262.66 s-1 mM-1, respectively. The enzyme showed a preference for p-NP stearate, tributyrin and canola oil. These biochemical features of SCNL suggested that it may be an excellent novel lipase candidate for industrial and biotechnological applications.
Keywords: Staphylococcus caprae; biochemical characterisation; lipase; purification.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



References
-
- Javed S, Azeem F, Hussain S, et al. . Bacterial lipases: a review on purification and characterization. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 2018;132:23–34. - PubMed
-
- Sarmah N, Revathi D, Sheelu G, et al. . Recent advances on sources and industrial applications of lipases. Biotechnol Prog 2018;34:5–28. - PubMed
-
- Sharma R, Soni SK, Vohra RM, et al. . Purification and characterisation of a thermostable alkaline lipase from a new thermophilic Bacillus sp. Rsj-1. Process Biochemistry 2002;37:1075–84.
-
- Lumor SE, Akoh CC.. Esterification and hydrolytic activities of candida rugosa lipase isoform 1 (lip1) immobilized on celite 545, duolite a7, and sephadex g-25. J Agric Food Chem 2008;56:10396–8. - PubMed
-
- Ji X, Chen G, Zhang Q, et al. . Purification and characterization of an extracellular cold-adapted alkaline lipase produced by psychrotrophic bacterium Yersinia enterocolitica strain KM1. J Basic Microbiol 2015;55:718–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
