Cellular and Mathematical Analyses of LUBAC Involvement in T Cell Receptor-Mediated NF-κB Activation Pathway
- PMID: 33329596
- PMCID: PMC7732508
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.601926
Cellular and Mathematical Analyses of LUBAC Involvement in T Cell Receptor-Mediated NF-κB Activation Pathway
Abstract
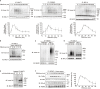
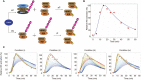
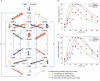
The LUBAC ubiquitin ligase complex, composed of the HOIP, HOIL-1L, and SHARPIN subunits, stimulates the canonical nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation pathways through its Met1-linked linear ubiquitination activity. Here we performed cellular and mathematical modeling analyses of the LUBAC involvement in the T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated NF-κB activation pathway, using the Jurkat human T cell line. LUBAC is indispensable for TCR-induced NF-κB and T cell activation, and transiently associates with and linearly ubiquitinates the CARMA1-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) complex, through the catalytic HOIP subunit. In contrast, the linear ubiquitination of NEMO, a substrate of the TNF-α-induced canonical NF-κB activation pathway, was limited during the TCR pathway. Among deubiquitinases, OTULIN, but not CYLD, plays a major role in downregulating LUBAC-mediated TCR signaling. Mathematical modeling indicated that linear ubiquitination of the CBM complex accelerates the activation of IκB kinase (IKK), as compared with the activity induced by linear ubiquitination of NEMO alone. Moreover, simulations of the sequential linear ubiquitination of the CBM complex suggested that the allosteric regulation of linear (de)ubiquitination of CBM subunits is controlled by the ubiquitin-linkage lengths. These results indicated that, unlike the TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation pathway, the TCR-mediated NF-κB activation in T lymphocytes has a characteristic mechanism to induce LUBAC-mediated NF-κB activation.
Keywords: CBM complex; LUBAC; NF-κB; T cell receptor; linear ubiquitin; mathematical model.
Copyright © 2020 Oikawa, Hatanaka, Suzuki and Tokunaga.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

