Universal scaling laws rule explosive growth in human cancers
- PMID: 33329756
- PMCID: PMC7116451
- DOI: 10.1038/s41567-020-0978-6
Universal scaling laws rule explosive growth in human cancers
Abstract
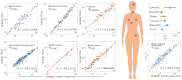
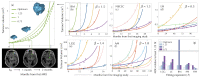
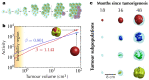
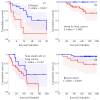
Most physical and other natural systems are complex entities composed of a large number of interacting individual elements. It is a surprising fact that they often obey the so-called scaling laws relating an observable quantity with a measure of the size of the system. Here we describe the discovery of universal superlinear metabolic scaling laws in human cancers. This dependence underpins increasing tumour aggressiveness, due to evolutionary dynamics, which leads to an explosive growth as the disease progresses. We validated this dynamic using longitudinal volumetric data of different histologies from large cohorts of cancer patients. To explain our observations we put forward increasingly-complex biologically-inspired mathematical models that captured the key processes governing tumor growth. Our models predicted that the emergence of superlinear allometric scaling laws is an inherently three-dimensional phenomenon. Moreover, the scaling laws thereby identified allowed us to define a set of metabolic metrics with prognostic value, thus providing added clinical utility to the base findings.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kleiber M. Body size and metabolism. Hilgardia. 1932;6:315–351.
-
- West G. Scale: The Universal Laws of Growth InnovationSustainabilityand the Pace of Life in OrganismsCitiesEconomies and Companies. Penguin Press; New York: 2017.
-
- West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ. A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science. 1997;276:122–126. - PubMed
-
- Savage VM, et al. The predominance of quarter-power scaling in biology. Funct Ecol. 2004;18:257–282.
-
- Reich PB, Tjoelker MG, Machado JL, Oleksyn J. Universal scaling of respiratory metabolismsize and nitrogen in plants. Nature. 2006;439:457–461. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
