Dispute cases related to pain management in Korea: analysis of Korea Medical Dispute Mediation and Arbitration Agency data
- PMID: 33329797
- PMCID: PMC7713854
- DOI: 10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.96
Dispute cases related to pain management in Korea: analysis of Korea Medical Dispute Mediation and Arbitration Agency data
Abstract
Background: Various developments in imaging techniques, interventional procedures, and medications for pain management have beneficial consequences. However, the nature of pain management often results in physicians becoming involved in medico-legal disputes with patients who purposely or accidentally bring litigation.
Methods: Data on medical disputes cases related to pain management were collected and analyzed through the Korea Medical Dispute Mediation and Arbitration Agency from 2012 to 2016.
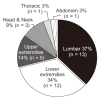
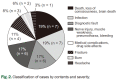
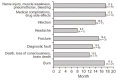
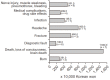
Results: In total, we identified 210 public-disclosed cases; of these, we identified 36 cases related to pain management. The department of orthopedics (n = 9, 25%) was the most related to these pain management cases. Pain management was most commonly offered for pain in the lumbar region (n = 13, 37%), lower extremities (n = 12, 34%), and for infection (n = 7, 19%). The time spent resolving disputes ranged from 8.0 to 17.5 months and the final settlement amount ranged from 1,800,000 to 15,000,000 Korean won. Causal relationships and medical malpractice were the most common controversial subjects of legal debate.
Conclusions: Various characteristics of medical disputes related to pain management in Korea were identified. Information regarding medical disputes in pain management should be available to help prevent further disputes and litigation, which is also useful to both patients and pain physicians. Guidelines and recommendations for pain management are needed, especially those focused on medico-legal cases.
Keywords: Compensation and redress; Complications; Dissent and disputes; Pain management; Wounds and injuries.
Copyright © the Korean Society of Anesthesiologists, 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Kim KH, Choi JW, Lee ES. The state of medical malpractice caused by private practice physicians (2010-2012): analysis through incident reports at Korean Medical Association Medical Indemnities Mutuals. J Korean Med Assoc. 2015;58:336–48. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2015.58.4.336. - DOI
-
- Lee JC, Min HY, Kim KH, Kim HN. Factors associated with the malpractice settlement cost between doctors and patients in Korea. Health Soc Sci. 2010;28:171–96.
-
- Lee IH, Lee IO. Questionnaire study about responsible parties in medical malpractice. Korean J Med Law. 2005;13:63–70.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources