Bleeding properties according to surgical sites during pediatric craniotomy: a retrospective study comparing the two stages of epilepsy surgery
- PMID: 33329826
- PMCID: PMC7713839
- DOI: 10.17085/apm.20010
Bleeding properties according to surgical sites during pediatric craniotomy: a retrospective study comparing the two stages of epilepsy surgery
Abstract
Background: During pediatric epilepsy surgery, due to low circulating blood volume, intraoperative bleeding can result in significant hemodynamic instability, thereby requiring meticulous hemodynamic and transfusion strategies. Knowing the source of bleeding during the procedure would allow medical staff to better prepare the perioperative protocols for these patients. We compared intraoperative bleeding between the first (involving skin to meninges) and second (involving brain parenchyma) stages of epilepsy surgery to investigate the differences between various anatomical sites.
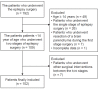
Methods: We reviewed the electronic medical records of 102 pediatric patients < 14 years old who underwent two-stage epilepsy surgeries during January 2012-December 2016. Invasive subdural grids were placed via craniotomy during Stage 1 and the epileptogenic zone was removed during Stage 2 of the surgery. We compared the volume of intraoperative bleeding between these two surgeries and identified variables associated with bleeding using multivariate regression analysis.
Results: Both surgeries resulted in similar intraoperative bleeding (24 vs. 26 ml/kg, P = 0.835), but Stage 2 required greater volumes of blood transfusion than Stage 1 (18.4 vs. 14.8 ml/kg, P = 0.011). Massive bleeding was associated with patients < 7 years of age in Stage 1 and weighing < 18 kg in Stage 2.
Conclusions: The volume of intraoperative bleeding was similar between the two stages of pediatric epilepsy surgery and was large enough to require blood transfusions. Thus, blood loss during pediatric epilepsy surgery occurred at both anatomic sites. This indicates the necessity of early preparation for blood transfusion in both stages of pediatric epilepsy surgery.
Keywords: Blood loss, surgical; Blood transfusion; Epilepsy; Neurosurgery; Pediatrics.
Copyright © the Korean Society of Anesthesiologists, 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic evaluation of intraoperative white matter tract shift in pediatric epilepsy surgery using high-field MRI and probabilistic high angular resolution diffusion imaging tractography.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017 May;19(5):592-605. doi: 10.3171/2016.11.PEDS16312. Epub 2017 Mar 17. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28304232
-
Tranexamic Acid Utilization in Craniosynostosis Surgery.Turk Neurosurg. 2020;30(3):407-415. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.27644-19.1. Turk Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32020570
-
Efficacy of intraoperative cell salvage systems in pediatric idiopathic scoliosis patients undergoing posterior spinal fusion with segmental spinal instrumentation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010 Jan 15;35(2):246-51. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181bdf22a. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010. PMID: 20081521
-
A model for predicting transfusion requirements in head and neck surgery.Laryngoscope. 1995 Aug;105(8 Pt 2 Suppl 73):1-17. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199508001-00001. Laryngoscope. 1995. PMID: 7630307 Review.
-
[Complications during epilepsy surgery. Experience after 102 interventions between 1997 and 2001].Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2003 Jun-Jul;50(6):267-73. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2003. PMID: 12940216 Review. Spanish.
References
-
- Vassal O, Desgranges FP, Tosetti S, Burgal S, Dailler F, Javouhey E, et al. Risk factors for intraoperative allogeneic blood transfusion during craniotomy for brain tumor removal in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2016;26:199–206. - PubMed
-
- Keung CY, Smith KR, Savoia HF, Davidson AJ. An audit of transfusion of red blood cell units in pediatric anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2009;19:320–8. - PubMed
-
- Kellermann TS, Wagner JL, Smith G, Karia S, Eskandari R. Surgical management of pediatric epilepsy: decision-making and outcomes. Pediatr Neurol. 2016;64:21–31. - PubMed
-
- Roth J, Carlson C, Devinsky O, Harter DH, Macallister WS, Weiner HL. Safety of staged epilepsy surgery in children. Neurosurgery. 2014;74:154–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources