Annular Elastolytic Giant Cell Granuloma
- PMID: 33329954
- PMCID: PMC7733766
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.11456
Annular Elastolytic Giant Cell Granuloma
Abstract
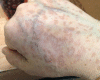
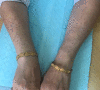
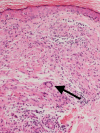
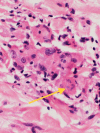
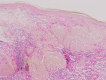
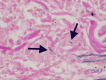
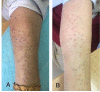
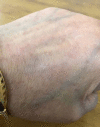
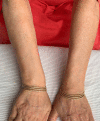
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG) is a rare, often self-limiting chronic inflammatory disorder mostly occurring in the sun-exposed areas such as the dorsum of hands, extensor surfaces of arms, face, anterior neck, and upper chest. The pathognomonic histological findings include the presence of numerous granulomas associated with loss of elastic fibers that appear to be ingested by multi-nucleated giant cells. Here, we present a case of a 56-year-old woman with multiple, anatomically variable erythematous lesions- annular and papular, mainly in the upper body. The clinical presentation and histopathologic findings support our diagnosis.
Keywords: actinic granuloma; annular; elastolysis; giant cell; sun exposure.
Copyright © 2020, Mistry et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Actinic granuloma. An annular connective tissue disorder affecting sun- and heat-damaged (elastotic) skin. O'Brien JP. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:460–466. - PubMed
-
- Is actinic granuloma a specific condition? Ragaz A, Ackerman AB. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/398673/ Am J Dermatopathol. 1979;1:43–50. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien actinic granuloma: a case report and brief review of literature. Coutinho ID, Ramos LI, Brites MM, Tellechea O. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4533541/ Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:391–393. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
