Novel Non-Coding Transcript in NR4A3 Locus, LncNR4A3, Regulates RNA Processing Machinery Proteins and NR4A3 Expression
- PMID: 33330042
- PMCID: PMC7719789
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.569668
Novel Non-Coding Transcript in NR4A3 Locus, LncNR4A3, Regulates RNA Processing Machinery Proteins and NR4A3 Expression
Abstract
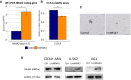
NR4A3 is a key tumor suppressor in myeloid malignancy, mice lacking both NR4A1 and family member NR4A3 rapidly develop lethal acute myeloid leukemia (AML). We identified a long non-coding transcript in the NR4A3 locus and pursued the characterization of this anonymous transcript and the study of its role in leukemogenesis. We characterized this novel long non-coding transcript as a sense polyadenylated transcript. Bone marrow cells from AML patients expressed significantly reduced levels of lncNR4A3 compared to healthy controls (controls = 15, MDS= 20, p=0.05., AML= 21, p<0.01). Expression of NR4A3, as previously reported, was also significantly reduced in AML. Interestingly, the expression of both coding and non-coding transcripts was highly correlated (Pearson R = 0.3771, P<0.01). Transient over-expression of LncNR4A3 by nucleofection led to an increase in the RNA and protein level of NR4A3, reduction of proliferation in myeloid cell lines K-562 and KG1 (n=3 and 2 respectively, p<0.05) and reduced colony formation capacity in primary leukemic cells. A mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics approach was used to identify proteins dysregulated after lncNR4A3 over-expression in K-562. Enrichment analysis showed that the altered proteins are biologically connected (n=4, p<0.001) and functionally associated to RNA binding, transcription elongation, and splicing. Remarkably, we were able to validate the most significant results by WB. We showed that this novel transcript, lncNR4A3 regulates NR4A3 and we hypothesize this regulatory mechanism is mediated by the modulation of the RNA processing machinery.
Keywords: NR4A3; RNA processing; acute myeloid leukemia; long non-coding RNA; myeloid malignancy.
Copyright © 2020 Congrains, Niemann, Duarte, Ferro and Olalla-Saad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

